Benzenesulfonic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
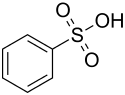
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Benzenesulfonic acid | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Benzene sulfonic acid ( IUPAC ) |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 6 O 3 S | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
Dissolving colorless tablets |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 158.18 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.32 g cm −3 (47 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point | ||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
171 ° C (at 0.13 hPa) |
|||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
0.7 |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water and ethanol , insoluble in non-polar solvents |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Benzene sulfonic acid is a chemical compound from the group of sulfonic acids . Their salts are called benzenesulfonates, pharmaceuticals also called besilates .
Extraction and presentation
Benzenesulfonic, by sulfonation of benzene with fuming sulfuric acid (with varying amounts of sulfuric trioxide be won):
use
Benzene sulfonic acid serves as a catalyst in chemical reactions and as an intermediate product in the production of resorcinol (via m - benzene disulfonic acid ) and phenol (by alkali melt).
INN nomenclature
In the medical and pharmaceutical sector, the internationally recognized short form for the anion of benzenesulfonic acid (benzenesulfonate) according to the INN rules is “Besilat”. Such short forms are created for molecular components if their systematic designation is too long. The “modified INN” (INNm) is created by combining a short form with the INN of the active component of the drug. One example is the drug amlodipine besylate , derived from the nitrogenous base amlodipine .
Derivatives
Derivatives of benzenesulfonic acid are, for example, anisolesulfonic acids and toluenesulfonic acids .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on benzenesulfonic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 13, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e record with benzenesulfonic acid in the GESTIS database of IFA , retrieved on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Joachim Buddrus: Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry , 4th edition, Walter de Gruyter Verlag, Berlin 2011, ISBN 978-3-11-024894-4 , p. 377.
- ↑ International Nonproprietary Names (INN) for pharmaceutical substances - Names for radicals, groups & others , WHO 2012.


