Yellow leek
| Yellow leek | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Yellow leek ( Allium flavum ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Allium flavum | ||||||||||||
| L. |
The yellow leek or yellow leek ( Allium flavum ) is a species of plant in the genus leek ( Allium ). It is widespread from southern Europe to the Middle East on dry hills, in German-speaking countries it is only native to Austria.
description
Vegetative characteristics
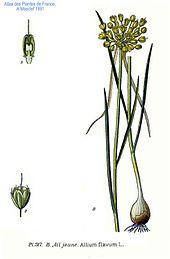
The yellow leek is a perennial, herbaceous plant that reaches heights of growth between 20 (rarely from 10) and 60 centimeters. The stem is erect or arched ascending.
The first half-stemmed, later hollow and narrow-linear leaves are up to 2 millimeters wide. They are smooth, blue frosted, weakly runny on top and shorter to as long as the stem. The leaves smell like garlic, but they don't taste hot.
Generative characteristics
The coarse shell is slightly herbaceous and two-lobed, with one valve usually being significantly longer than the other; it is narrowly linear to almost bristle-like and usually many times longer than the inflorescence. Many flowers stand loosely together in a shingled inflorescence . There are no brood bulbs on the inflorescences.
The flowering period extends from June to August. The almost thread-like flower stalks are up to three times as long as the flowers. The flowers are threefold. The yellow tepals are blunt, oblong, 4 to 5 millimeters long and more or less shiny. The stamens are always and up to twice as long as the tepals. They are fused with each other and with the perigone at the base. The stylus is elongated.
The capsule fruit is ovate and strongly three-sided.
The number of chromosomes is 2n = 16, less often 32.
ecology
In Allium flavum is a geophytes .
Allium flavum serves the leek silk bee ( Colletes graeffei ) exclusively as a food source.
Occurrence
The yellow leek is native to Eurasia and has a meridional to submeridional distribution here.
In Central Europe, the yellow leek is rarely to be found scattered from the plain to the foothills of the Alps at altitudes of 1000 meters. It colonizes dry hills in sunny places, especially on lime and trachyte as subsoil. It is not at home in Germany or Switzerland. In the Franconian Forest and at the Kaiserstuhl it occurs as an unstable neophyte . It is a species of character of the order Festucetalia valesiacae. In Austria it can be found in Lower Austria, Vienna and Burgenland, where it occurs scattered or rarely in the dry grasslands and dry meadows of the Pannonian region . In addition, it occurs from Spain via the eastern Czech Republic and Hungary to southern Russia, the Caucasus and the Middle East.
Systematics
Allium flavum was first published by Carl von Linné . An important synonym for Allium flavum L. is Cepa flava (L.) Moench . Allium flavum belongs to the Codonoprasum section of the subgenus Allium in the genus Allium . The dwarf form Allium flavum var. Webbii (Clementi) Nyman was described as a variety , it is no longer recognized today.
One can distinguish the following subspecies and varieties:
- Allium flavum subsp. flavum : It occurs from southern Central Europe and southern Europe to western Turkey.
- Allium flavum subsp. ionochlorum Maire : It occurs in Morocco and Algeria.
- Allium flavum var. Minus Boiss. : It occurs in northern Turkey.
- Allium flavum var. Pilosum Kollmann & Koyuncu : It occurs in southern Turkey.
- Allium flavum subsp. tauricum (Better ex Rchb.) K. Richt. : It occurs from Southeast Europe to Iran.
proof
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Karl Suessenguth: Illustrated flora of Central Europe. With special consideration of Greater Germany, Switzerland and the neighboring areas. For use in schools and for self-teaching. Founded by Gustav Hegi . 2nd, revised edition. Volume II: Monocotyledones, Part II. JF Lehmanns, Munich / Berlin 1939, pp. 282–283
- ^ A b Manfred A. Fischer , Karl Oswald, Wolfgang Adler: Excursion flora for Austria, Liechtenstein and South Tyrol. 3rd, improved edition. State of Upper Austria, Biology Center of the Upper Austrian State Museums, Linz 2008, ISBN 978-3-85474-187-9 .
- ↑ a b Erich Oberdorfer : Plant-sociological excursion flora for Germany and neighboring areas. 8th edition, Verlag Eugen Ulmer, Stuttgart 2001, ISBN 3-8001-3131-5 . P. 131.
- ↑ Herbert Zettel, Heinz Wiesbauer: Wild bees (Apidae) Pannonian dry grasslands. In: Heinz Wiesbauer (Hrsg.): The steppe is alive - rock steppes and dry grasslands in Lower Austria , St. Pölten 2008, p. 63, ISBN 3-901542-28-0 .
- ^ A b Werner Rothmaler: Excursion flora from Germany. Volume 4. Vascular Plants: Critical Volume . 10th edition, Elsevier, Munich 2005, ISBN 3-8274-1496-2
- ↑ N. Friesen et al .: Phylogeny and new intrageneric classification of Allium (Alliaceae) based on nuclear ribosomal DNA ITS sequences. In: Aliso , Volume 22, 2006, pp. 372-395.
- ↑ a b c d e f Rafaël Govaerts (Ed.): Allium - data sheet at World Checklist of Selected Plant Families of the Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Last accessed on September 22, 2016.
Web links
- Allium flavum L., yellow leek. In: FloraWeb.de.
- Yellow leek . In: BiolFlor, the database of biological-ecological characteristics of the flora of Germany.
- Profile and distribution map for Bavaria . In: Botanical Information Hub of Bavaria .
- Thomas Meyer: Data sheet with identification key and photos at Flora-de: Flora von Deutschland (old name of the website: Flowers in Swabia )
- Allium flavum at Plants For A Future
- Data sheet with distribution and photos at Flora Italiana by Schede di Botanica .
- Data sheet on yellow leek at Botanik in the picture - Flora of Austria .
- Distribution map at Euro + Med .