Alosetron
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
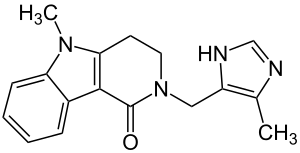
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Alosetron | ||||||||||||
| other names |
5-methyl-2 - [(4-methyl-1 H -imidazol-5-yl) methyl] -3,4-dihydro-2 H -pyrido [4,3- b ] indol-1 (5 H ) -one ( IUPAC ) |
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula |
|
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
selective blockade of central 5-HT 3 receptors |
||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | |||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
238-240 ° C
|
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Alosetron (trade name: Lotronex ® (USA); manufacturer: Prometheus ) is a drug from the Setrone group that is used in the USA to treat irritable bowel syndrome . The active ingredient was patented by Glaxo Wellcome in 1989 as an ulcer agent . We used the hydrochloride .
Clinical information
Application areas (indications)
In the United States, alosetron can be used to treat women who have severe irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea as the main symptom , if they have
- Have irritable bowel symptoms for 6 months or more
- no anatomical or biochemical abnormalities of the digestive tract have and
- did not respond adequately to the usual treatment.
Alosetron has not been adequately studied in men.
Doctors who want to prescribe Alosetron must register with the manufacturer in a register of prescribers and provide comprehensive information before prescribing the drug and conclude a written patient-doctor agreement with the patient.
Adverse effects (side effects)
Constipation occurs in up to 30% of patients . Other common side effects are nausea , malaise, or stomach pain. Approximately one to two patients in 1000 treated (1–2 ‰) developed severe constipation requiring surgery and ischemic intestinal inflammation , e. T. with fatal consequences.
Pharmacological properties
Mechanism of action (pharmacodynamics)
Alosetron is a selective inhibitor of the 5-HT 3 receptors ( serotonin receptors). These occur in particularly high density in the gastrointestinal tract. Like other 5-HT 3 receptor antagonists, alosetron is effective against vomiting, at least in animal experiments. In addition, alosetron slows the movement of stool through the intestinal tract . Because of this pharmacological property, alosetron is used in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome.
History
Alosetron was developed by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) and approved for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome in early 2000 after just seven months of processing the application for approval by the US Food and Drug Administration . After only nine months, it was temporarily withdrawn from the market at the end of 2000 due to severe constipation requiring surgery, ischemic intestinal inflammation and death. Lotronex has been back on the market in the USA since mid-2002 with restricted approval and conditions. Thus, Alosetron, in addition to z. B. bupropion and natalizumab , one of the few active ingredients that came back on the market after being recalled due to safety concerns.
It is not known whether an application for EU approval has ever been made.
At the end of 2007, GSK sold Lotronex to the Californian company Prometheus.
criticism
The FDA's way of working was criticized in an unusually harsh form in an editorial in the renowned British medical journal Lancet by its editor Richard Horton, using the example of alosetron. Horton accused the FDA of becoming "industry stooges."
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on Alosetron. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 27, 2019.
- ^ The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals . 14th edition. Merck & Co., Whitehouse Station NJ 2006, p. 55, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 .
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ Prometheus Laboratories Inc. Prescribing Information Lotronex. As of April 2008.
- ^ M Camilleri: Pharmacology and clinical experience with alosetron . In: Expert Opin Investig Drugs . 9, No. 1, January 2000, pp. 147-159. doi : 10.1517 / 13543784.9.1.147 . PMID 11060667 .
- ↑ Press release of November 7, 2007. ( Memento of July 14, 2012 in the web archive archive.today ) Prometheus Laboratories Inc. (English) accessed on August 27, 2008.
- ^ R. Horton: Lotronex and the FDA: a fatal erosion of integrity . In: Lancet , 2001, 357, pp. 1544-1545; PMID 11377636 .