Ammonium hydrogen carbonate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
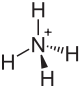 
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Ammonium hydrogen carbonate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | NH 4 HCO 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white, crystalline powder with an ammonia-like odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 79.06 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.58 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
Decomposition from 60 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−849 kJ mol −1 |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Ammonium hydrogen carbonate (including A mmonium b i c arbonat, ABC engine) is an ammonium salt of carbonic acid . It is the main component of staghorn salt .
Occurrence
In nature, ammonium hydrogen carbonate is found as the mineral teschemacherite , as well as in guano deposits on the west coast of Patagonia and on the Chincha Islands .
Extraction and presentation
It is manufactured by introducing carbon dioxide into concentrated ammonia solution at 35 to 40 ° C. The precipitated crystalline ammonium hydrogen carbonate is centrifuged off and dried at a temperature of 40.degree.
properties
Ammonium hydrogen carbonate forms colorless prismatic crystals that appear in a rhombic crystal lattice. The salt dissolves very well in water . The solubility increases with the temperature.
| Solubility of ammonium hydrogen carbonate in water | ||||||||||||
| temperature | in K | 273.2 | 283.2 | 293.2 | 303.2 | 313.2 | 323.2 | 333.2 | ||||
| in ° C | 0 | 10 | 20th | 30th | 40 | 50 | 60 | |||||
| solubility | in% | 10.6 | 13.9 | 17.8 | 22.1 | 26.8 | 31.6 | 37.2 | ||||
The pH value of an aqueous solution (50 g / l at 20 ° C) is approx. 8. Even at room temperature, a slow breakdown into ammonia, carbon dioxide and water can be observed. The rate of disintegration increases sharply with increasing temperature.
The decay can be quantified via the corresponding dissociation pressures.
| Dissociation pressure of ammonium hydrogen carbonate | ||||||||||||
| temperature | in K | 298.6 | 307.4 | 313.9 | 318.2 | 323.2 | 329.0 | 332.5 | ||||
| in ° C | 25.45 | 34.25 | 40.75 | 45.05 | 50.05 | 55.85 | 59.35 | |||||
| pressure | in kPa | 7.85 | 16.26 | 26.79 | 37.06 | 52.65 | 82.11 | 108.64 | ||||
use
Since it has a defined composition, it is more suitable than deer horn salt as a raising agent ("ABC-Trieb" / baking powder) for the production of Christmas cookies such as gingerbread and speculoos in large-scale automated baking systems . It is approved in the EU as a food additive with the number E 503ii and comes on the market with the purest additive .
The ufo-shaped pieces of cake "American" owe their name to this raising agent . According to this controversial theory, these pieces of cake were originally called "ammonia cans". A baker is said to have exchanged this monstrous word for “Americans”. (other theories on this under Americans (pastries) )
In the People's Republic of China , ammonium hydrogen carbonate was previously used in large quantities as the most important nitrogen fertilizer . Production began in 1958 and took place in over 1000 small systems. In the meantime it has mainly been replaced by urea , but in 2012 the market share was still 17%.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on ammonium hydrogen carbonate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c Entry on ammonium hydrogen carbonate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on October 14, 2014.
- ↑ PAETEC Formula Collection Edition 2003, p. 116.
- ↑ a b Brockhaus ABC chemistry. FA Brockhaus Verlag, Leipzig 1971, p. 73.
- ↑ a b c K.-H. Zapp, K.-H. Wostbrock, M. Schäfer, K. Sato, H. Seiter, W. Zwick, R. Creutziger, H. Head: Ammonium Compounds. In: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry . Wiley-VCH Verlag, Weinheim 2005. doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a02_243 .
- ↑ Ching-Kwei Li, Rong-Yen Chen: Ammonium bicarbonate used as a nitrogen fertilizer in China . In: Fertilizer Research . tape 1 , no. 3 , 1980, p. 125-136 , doi : 10.1007 / BF01053127 .
- ↑ Yara Fertilizer Industry Handbook 2014 ( Memento from May 17, 2017 in the Internet Archive ), p. 25.

