Cobalt yellow
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cobalt yellow | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
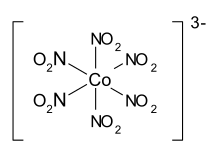
| Molecular formula | K 3 [Co (NO 2 ) 6 ] • 1.5 H 2 O | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
deep yellow, shiny prisms and double pyramids |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 479.28 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
5.18 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water, decomposes in hot water |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
color code: # E2DC30
Cobalt yellow , also called aureolin (from Latin aureolus, “beautifully made of gold”) after its golden yellow color , is a fine, light crystalline powder and is used as a pigment for oil and watercolor painting .
The color index value of cobalt yellow is PY40. This stands for Pigment Yellow 40 , which is the fortieth entry in the list of yellow pigments.
history
Cobalt yellow was invented by Nikolaus Wolfgang Fischer in 1848 and has been manufactured industrially since around 1860. At that time, it was the only glaze color with a bright yellow color besides Indian yellow. It was not until the invention of organic tar dyes , which were much cheaper to produce, that its spread declined again.
Chemical properties
From a chemical point of view, aureolin is potassium hexanitritocobaltate (III) - with the formula K 3 [Co (NO 2 ) 6 ] · 1.5 H 2 O. It should only be used in neutral, as it is not used in an acidic or basic environment is constant.
It separates out as a precipitate when a sodium hexanitritocobaltate (III) solution is added dropwise to a solution containing potassium ions (e.g. dissolved potassium nitrate ). The sodium hexanitritocobaltate (III) is in turn obtained by a previous oxidation of the Co 2+ with air ( oxygen ) to Co 3+ in a solution of sodium nitrite , cobalt (II) nitrate and acetic acid:
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on potassium hexanitrocobaltate (III). In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 14, 2014.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ "Nitrous oxide cobalt oxide potash": NW Fischer: About the nitrous acid salts . In: Annals of Physics and Chemistry . tape 150 , no. January 5 , 1848, p. 115-125 , doi : 10.1002 / andp.18491500512 .
- ↑ a b 43500 cobalt yellow, aureolin. (PDF, 43 kB) Kremer Pigments, accessed on October 24, 2015 .
- ^ Heinrich Remy: Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry Volume I + II, Leipzig 1973, p. 400.

![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {\ 4 \ Na_ {3} [Co (NO_ {2}) _ {6}] \ +8 \ NaNO_ {3} \ +4 \ CH_ {3} COONa \ +2 \ H_ {2 } O}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bd7d6eeda05ea98b8141a3e00dfcc2702564529c)
![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {Na_ {3} [Co (NO_ {2}) _ {6}] \ +3 \ KNO_ {3} \ longrightarrow \ K_ {3} [Co (NO_ {2}) _ {6} ] \ downarrow \ +3 \ NaNO_ {3}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e1c0c41a62b9ba0a9fd978fc78da5fb6989e109b)
