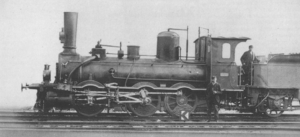
Badische X a (old)
| X a VIIb (from 1868) |
|
|---|---|
|
No. 77 Feldberg
|
|
| Numbering: | 77-82 |
| Number: | 6th |
| Manufacturer: | MBG Karlsruhe |
| Year of construction (s): | 1855/1856 |
| Retirement: | 1881-1891 |
| Type : | C n2 |
| Gauge : | 1435 mm ( standard gauge ) |
| Length over buffers: | 13,508 mm |
| Height: | 4,200 mm |
| Total wheelbase: | 3,450 mm |
| Empty mass: | 29.9 t |
| Service mass: | 32.6 t |
| Friction mass: | 32.6 t |
| Wheel set mass : | 10.9 t |
| Top speed: | 45 km / h |
| Coupling wheel diameter: | 1,220 mm |
| Control type : | Stephenson |
| Number of cylinders: | 2 |
| Cylinder diameter: | 408 mm |
| Piston stroke: | 610 mm |
| Boiler overpressure: | 7 kg / cm² 68.6 kN / cm² |
| Number of heating pipes: | 191 |
| Heating pipe length: | 4,220 mm |
| Grate area: | 1.04 m² |
| Radiant heating surface: | 6.77 m² |
| Tubular heating surface: | 107.62 m² |
| Evaporation heating surface: | 114.39 m² |
| Locomotive brake: | Screw brake on the tender |
The machines of type X a , from 1868 VII b, were freight locomotives of the Grand Ducal Baden State Railways .
The expected traffic volumes for 1856 made it necessary to purchase new freight locomotives. It was decided against the Crampton construction and commissioned the construction of six triple-coupled locomotives. With this series began a whole series of C-couplers, which handled the freight traffic of the Baden Railway for many years. The locomotives were able to pull a 654-ton train at 23 km / h on an incline of 0.33%. They had a smooth and stable run. The locomotives were deployed from Freiburg. After being forced out of operations, some of the machines could still be found for a while when they were being pushed on the Odenwaldbahn and in the Mannheim harbor. The first locomotives were taken out of service in 1881. The last machines were temporarily used after 1891 as written off locomotives (the company number was increased by 1000) and then also scrapped.
Constructive features
The locomotives had a single fork frame with inner 21 mm thick fork plates for the rear axles. The Crampton kettle had two domes and was arranged relatively low with 1,530 mm kettle center above the top of the rails. The boiler was later rebuilt and the boiler pressure increased from 7 to 8 bar. Since the standing boiler ceiling was connected to the fire box ceiling by stud bolts, the rear dome was moved forward. The front dome was replaced by a regulator attachment. The boiler water was fed by pumps driven by eccentrics from the drive axles.
The two-cylinder wet steam engine was arranged on the outside and acted on the central coupling axis. The drive rods were forked. The two rear axles were suspended by means of joint leaf springs hanging down, and the front axle by means of long springs.
The locomotives were equipped with type 3 T 5.62 tenders
Footnotes
- ↑ To distinguish the locomotives designated according to the 1868 scheme, also designated as X a (old) .
literature
- Hermann Lohr, Georg Thielmann: Baden locomotive archive . transpress, Berlin 1988, ISBN 3344002104