Bensulide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
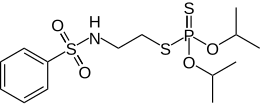
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Bensulide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 14 H 24 NO 4 PS 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 397.52 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.25 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
34.5 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
200 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Bensulide is a chemical compound from the group of sulfonic acid amides and thiophosphoric acid esters .
history
Bensulide was marketed in the United States in 1964 for the control of foxgloves and annual bluegrass on lawns by the Gowan Company. In 1968 the patent for the control of grasses in agriculture followed. About 250 tons are used annually in the USA.
Extraction and presentation
Bensulide can be obtained by a multi-stage reaction from phenylsulfonyl chloride (is made to react with ethanolamine and thionyl chloride ) and phosphorus (V) sulfide (is made to react with isopropanol and ammonium hydroxide ).
properties
Bensulide is a colorless solid that is practically insoluble in water. It decomposes from a temperature of 200 ° C. The technical product is a viscous amber-colored liquid from a temperature of 34 ° C. Bensulide acts as a cholinesterase inhibitor and thus has negative effects on the central nervous system.
use
Bensulide is used as a herbicide on a number of fruits and vegetables. Trade names are Betamec, Betasan, Disan, Exporsan, Prefar and Pre-san.
Admission
In the EU countries such as Germany and Austria as well as in Switzerland, no pesticides containing bensulide are permitted.
Web links
- Office of Pesticide Programs: Bensulide - Analysis of Risks to Endangered and Threatened Salmon and Steelhead
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on bensulide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on June 2, 2011(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c Environmental Protection Agency: Interim reregistration eligibility decision (IRED) Bensulide ( limited preview in the Google book search).
- ↑ Entry on Bensulide in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Bensulide data sheet at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 20, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger; Pesticide synthesis handbook, p. 343; ISBN 978-0-81551401-5 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ^ Extension Toxicology Network: Bensulide
- ^ Larry Turner, Environmental Field Branch Office of Pesticide Programs, Bensulide - Analysis of Risks to Endangered and Threatened Salmon and Steelhead .
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Bensulide in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; Retrieved March 3, 2016.


