Bindschedler's green
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
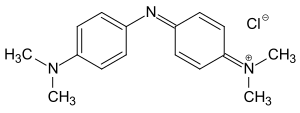
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Bindschedler's green | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 16 H 20 ClN 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 289.81 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Bindschedler's green is a green dye from the indamine group . It is produced by condensation of N , N -dimethylaniline with 4-nitroso- N , N -dimethylaniline or by oxidative coupling of N , N -dimethylaniline with 4-amino- N , N -dimethylaniline with sodium dichromate as the oxidizing agent and bears the name of his Explorer Robert Bindschedler .
Bindschedler's green can be used for the quantitative determination of hydrogen sulfide , as it reacts with this completely to form methylene blue , which can be detected photometrically at 680 nm. The absorption maximum of Bindschedler's green is 727 nm . This absorption band can be shifted further into the longer-wave range by modifications. Various indamine dyes with a basic structure derived from Bindschedler's green absorb in the near infrared range ( NIR ).
Various assays have been developed on the basis of Bindschedler's green , for example a cytotoxicity assay. The compound can also be used to measure the activity of dehydrogenase .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b data sheet BINDSCHEDLERS GREEN, INDICATOR GRADE from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 13, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on indamine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 29, 2014.
- ↑ H. Wieland, in: Ber. d. dt. Chem. Ges. 1915 , 48 , p. 1078.
- ↑ HJ Shine, RL Snell, JC Trisler: Nature of Bindschedler's Green: preparation for analysis of hydrazo compounds , in: Anal. Chem. 1958 , 30 , pp. 383-384.
- ^ A b J. Griffiths, R. Cox: Light absorption and stability properties of some near-IR indamine dyes related to Bindschedler's green , in: Dyes and Pigments 1999 , 42 , pp. 29-34.
- ↑ F. Tietze, T. Eicher, reactions and syntheses in the organic-chemical internship and research laboratory , 2nd edition, ISBN 978-3-527-30874-3 (paper), ISBN 978-3-527-60171-4 (online )
- ↑ T. Schödl: Sulphide-Quinone Reductase (SQR) from Aquifex aeolicus: gene synthesis, expression, purification and biochemical characterization , dissertation, Regensburg 2003 , p. 65
- ↑ K. Takagi in: A sensitive colorimetric assay for polyamines in erythrocytes using oat seedling polyamine oxidase , in: Clin. Chim. Acta 2004 , 340 , pp. 219-227.
- ↑ S. Yamashoji: A cytotoxicity assay with Bindschedler's green leuco base , in: Anal. Biochem. 1996 , 240 , pp. 310-312; PMID 8811930
- ↑ MD Smith, CL Olson: Differential amperometric measurement of serum lactate dehydrogenase activity using Bindschedler's green , in: Anal. Chem. 1974 , 46 , pp. 1544-1547; PMID 4412813
