Lead (IV) fluoride
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Pb 4+ __ F - | ||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
tetragonal |
|||||||||||||||
| Space group |
I 4 / mmm (No. 139) |
|||||||||||||||
| Lattice parameters |
a 425.36 pm, c 806.4 pm, Z = 2 |
|||||||||||||||
| Coordination numbers |
[6] Pb |
|||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Lead (IV) fluoride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Lead tetrafluoride |
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | PbF 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 283.18 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
6.7 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
~ 600 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Lead (IV) fluoride is an inorganic chemical compound of lead from the group of fluorides .
Extraction and presentation
Lead (IV) fluoride can be obtained by reacting lead (II) fluoride or lead with fluorine .
properties
Lead (IV) fluoride is a white, crystalline solid that is very sensitive to moisture. In humid air it immediately turns brown due to the formation of lead dioxide .
This reaction also happens in dilute hydrofluoric acid ; in concentrated hydrofluoric acid (or pure hydrogen fluoride ), lead fluoric acid ("fluoroplumbic acid") is formed.
The salts of this acid can also be prepared.
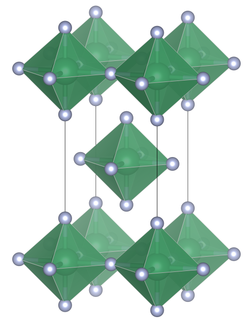
Lead (IV) fluoride has a tetragonal crystal structure with the space group I 4 / mmm (space group no.139 ) and the lattice constants a 425.36 pm, c 806.4 pm, and Z = 2. The compound exists like tin ( IV) fluoride of PbF 6 - octahedra the on common equatorial bridges each having four PbF 6 octahedra are linked to planar layers.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d data sheet Lead (IV) fluoride, 99% from AlfaAesar, accessed on September 24, 2013 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Georg Brauer (Ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler a . a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume I, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , p. 233.
- ^ Jean d'Ans, Ellen Lax, Roger Blachnik: Pocket book for chemists and physicists . Springer DE, 1998, ISBN 3-642-58842-5 , pp. 660 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 101st edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1995, ISBN 3-11-012641-9 , p. 970.
- ↑ M. Bork, R. Hoppe: On the structure of PbF4 with structure refinement on SnF4. In: Journal of Inorganic and General Chemistry. 622, 1996, pp. 1557-1563, doi : 10.1002 / zaac.19966220919 .







