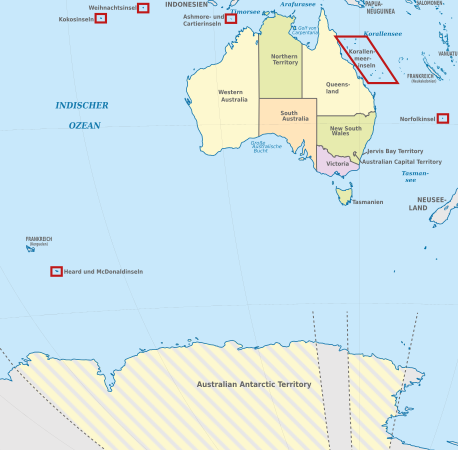
States, territories and outskirts of Australia
A state , territory or outlying area is a member state of the federally organized Commonwealth of Australia .
In addition to the six federal states (five continental and Tasmania ) and the three continental territories , of which the youngest ( Jervis Bay Territory ) was not formed until 1989 when it was split off from the capital territory , there are seven Australian outer areas (six islands / archipelagos and part of Antarctica ). While the states are largely independent, the territories have a much lower degree of autonomy or are directly subordinate to the federal government.
overview
| Reference cards | |
|---|---|
| Areas | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| designation | Abbreviation | Postcode | Postcode | Type | Capital (or largest settlement) | population | Area in km² |
|
|
Outdoor area | (West Islet) | 0 | 199 | |||
|
|
TAS | 7151 | Outdoor area | ( Mawson Station ) | 1,000 | 5,896,500 | |
|
|
AU-ACT | ACT | 0200-0299 2600-2618 2900-2920 |
territory | Canberra | 358,894 | 2,358 |
|
|
CX | WA | 6798 | Outdoor area | Flying Fish Cove | 1,493 | 135 |
|
|
CC | WA | 6799 | Outdoor area | West Iceland | 628 | 14th |
|
|
Outdoor area | ( Willis Island ) | 4th | 10 | |||
|
|
HM | Outdoor area | (Atlas Cove) | 0 | 372 | ||
|
|
JBT | territory | ( Jervis Bay Village ) | 611 | 70 | ||
|
|
AU-NSW | NSW | 1000-2599 2619-2898 2921-2999 |
State | Sydney | 7,238,819 | 800,642 |
|
|
NF | NSW | 2899 | Outdoor area | Kingston | 2.114 | 35 |
|
|
AU-NT | NT | 0800-0899 0900-0999 |
territory | Darwin | 229,675 | 1,349,129 |
|
|
AU-QLD | QLD | 4000-4999 9000-9999 |
State | Brisbane | 4,516,361 | 1,730,648 |
|
|
AU-SA | SA | 5000-5999 | State | Adelaide | 1,644,642 | 983.482 |
|
|
AU-TAS | TAS | 7000-7150 7152-7999 |
State | Hobart | 507.626 | 68,401 |
|
|
AU-VIC | VIC | 3000-3999 8000-8999 |
State | Melbourne | 5,547,527 | 227,416 |
|
|
AU-WA | WA | 6000-6797 6999 |
State | Perth | 2,296,411 | 2,529,875 |
Properties of states and territories
The states emerged from independent British colonies that existed before Australia's independence in 1901. Their rights are protected by the Australian constitution , they each have their own constitution and parliament with extensive rights. Federal laws only apply in the areas in which the federal constitution expressly allows them.
The territories, on the other hand, are under the constitution in principle directly subordinate to the Australian Parliament, which has full legislative power there. The outer areas are also administered directly by the federal government, while the Northern Territory , Australian Capital Territory (ACT) and Norfolk Island on the Australian continent have their own administration. The Jervis Bay Territory is a special case. It has no self-government, but is administered partly by the federal government and partly by the Australian Capital Territory (ACT). The federal government has the right to overrule laws enacted by the administration there in the self-governing territories, which it has done in a few rare cases (e.g. the Rights of the Terminally Ill Act of the Northern Territory).
Each state has a governor who is appointed by Queen Elizabeth II as head of state of Australia. The Northern Territory and Norfolk Island, on the other hand, are each represented by a representative appointed by the Governor General of Australia . The Australian Capital Territory (ACT) has neither a governor nor a representative. There the governor general exercises certain rights that accrue to the respective governor in the states. This includes, for example, the right to be able to dissolve parliament.
Queensland abolished its upper house in 1922, the other states have a bicameral parliament . The elections for the lower house, the Legislative Assembly or House of Assembly is called, are based on the majority vote held only in Tasmania which is proportional representation applied. The House of Lords, known as the Legislative Council , is also elected using proportional representation. The three self-governing territories have a unicameral parliament.
The government of each Australian state is headed by a prime minister appointed by the majority party that forms the government and appointed by the state governor. The head of government of the self-governing territories is called the Chief Minister .