Cadmium fluoride
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Cd 2+ __ F - | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cadmium fluoride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | CdF 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 150.41 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
6.64 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
1078 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
1748 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
10 h Pa (1257 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Authorization procedure under REACH |
particularly worrying : carcinogenic, mutagenic, toxic for reproduction ( CMR ), serious effects on human health are considered likely |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Cadmium fluoride is a chemical compound from the group of fluorides .
Extraction and presentation
Cadmium fluoride can be obtained by reacting cadmium carbonate with hydrofluoric acid .
properties
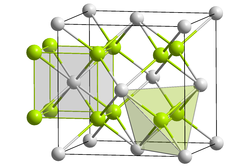
Cadmium fluoride has a cubic crystal structure of the fluorite type. Thin films of cadmium fluoride show photoluminescence . The compound begins to decompose at temperatures above 1000 ° C.
use
Cadmium fluoride is used as an insulator in high-frequency semiconductor technology and is also found in fluorite glasses .
safety instructions
Cadmium fluoride is highly toxic and, like many cadmium compounds, is classified as carcinogenic and germ cell mutagenic. The main routes of intake are the respiratory and digestive tracts; absorption through the skin is also possible.
literature
- T. Dote, K. Adachi, E. Yamadori, M. Imanishi, H. Tsuji, E. Tanida, K. Kono: Abnormalities in cadmium fluoride kinetics in serum, bile, and urine after single intravenous administration of toxic doses to rats. In: Journal of occupational health. Volume 50, Number 4, 2008, pp. 339-347, PMID 18525160 . PDF
- Paul F. Weller: Electrical and Optical Properties of Rare Earth Doped Cadmium Fluoride Single Crystals. In: Inorganic Chemistry. 4, 1965, p. 1545, doi : 10.1021 / ic50033a004 .
- BA Orlowski, P. Plenkiewicz: Electronic Band Structure of CdF 2 . Photoemission Experiment and Pseudopotential Calculations. In: physica status solidi. 126, 1984, p. 285, doi : 10.1002 / pssb.2221260134 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on cadmium fluoride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ^ H. Kojima, SG Whiteway, CR Masson: Melting points of inorganic fluorides . In: Canadian Journal of Chemistry . 46 (18), 1968, pp. 2968-2971, doi : 10.1139 / v68-494 .
- ^ CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 96th Edition . CRC Press, 2015, ISBN 978-1-4822-6097-7 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ a b c Georg Brauer (ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler a . a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume I, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 .
- ↑ Entry on cadmium fluoride in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Entry in the SVHC list of the European Chemicals Agency , accessed on March 19, 2015.
- ↑ Free Patent Online: Electroluminescent unit



