Cadmium carbonate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
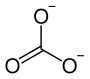
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cadmium carbonate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Cadmium carbonate |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | CdCO 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 172.42 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
4.258 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
357 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Authorization procedure under REACH |
particularly worrying : carcinogenic, mutagenic ( CMR ), serious effects on human health are considered likely |
|||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−750.6 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Cadmium carbonate is a chemical compound from the group of carbonates .
Occurrence
Cadmium carbonate occurs naturally in the form of the mineral otavite and as zinc cadmium carbonate cadmium smithsonite (Zn, Cd) CO 3 .
Extraction and presentation
Cadmium carbonate can be produced by reacting a cadmium chloride solution with ammonium carbonate and then dissolving the resulting precipitate with ammonia .
Cadmium carbonate can also be obtained by reacting a cadmium chloride solution with concentrated hydrochloric acid and urea .
properties
Cadmium carbonate is a non-flammable, white, odorless solid that decomposes at temperatures above 357 ° C, producing cadmium oxide and carbon dioxide . It has a trigonal crystal structure of the calcite type with the space group R 3 c (space group no. 167) and the lattice parameters a = 4.920 and c = 16.298 Å .
use
Cadmium carbonate is used to make cadmium oxide and other cadmium salts (such as the pigments cadmium yellow and cadmium red ).
safety instructions
At the suggestion of the Swedish Chemicals Agency, the chemical classification of cadmium carbonate was revised in 2015. The Committee for Risk Assessment (RAC) of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) changed the classification for cadmium carbonate as follows on December 4th: Cadmium carbonate is classified as carcinogenic Carc 1B, mutagenic Muta 1B and STOT RE 1, the additional warnings were set to H 340 , H350 and H372 (kidney, bone). This classification of the RAC has yet to be implemented by the EU Commission into applicable law, but with the publication it represents the state of knowledge that must be taken into account by companies and authorities.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on cadmium carbonate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Georg Brauer (Ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler a . a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume II, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1978, ISBN 3-432-87813-3 .
- ↑ a b Cadmium carbonate at Todini and Co. ( Memento from February 12, 2013 in the web archive archive.today )
- ↑ Entry on cadmium carbonate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on December 15, 2019. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Entry in the SVHC list of the European Chemicals Agency , accessed on January 19, 2018.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-19.
- ↑ Mineralienatlas: Otavit , accessed on February 4, 2018.
- ↑ RAC decision of December 4, 2015



![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {CdCl_ {2} + (NH_ {4}) _ {2} CO_ {3} + NH_ {3} \ longrightarrow [Cd (NH_ {3}) _ {4}] CO_ {3} + NH_ {4} Cl}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0271e11559d89db999c4b55aa8e5c5026049115d)
![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {[Cd (NH_ {3}) _ {4}] CO_ {3} \ longrightarrow CdCO_ {3} +4 \ NH_ {3}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9d0cfe303a1bc5185c78905ca2db6f362058d0da)
