Cadmium oxide
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| __ Cd 2+ __ O 2− | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cadmium oxide | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | CdO | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
red-brown, odorless solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 128.41 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density | |||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
1559 ° C (sublimation amorphous) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water (49 mg l −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Authorization procedure under REACH |
particularly worrying : carcinogenic ( CMR ), serious effects on human health are considered likely |
||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Cadmium oxide is a chemical compound of cadmium and is one of the oxides . It occurs in two different forms as an amorphous powder or a crystalline compound, which differ significantly in their properties.
Occurrence
Cadmium oxide occurs naturally in the form of the rare mineral monteponite .
Extraction and presentation
Cadmium oxide can be obtained by oxidizing cadmium vapor with oxygen or cadmium melts with other oxidizing agents.
Alternatives are the thermal decomposition of cadmium carbonate or cadmium nitrate . Even when roasting of cadmium sulfide produced cadmium.
properties
Amorphous cadmium oxide is a yellow, depending on the particle size, brown to black powder with a density of 6.95 g · cm −3 . It is easily reducible and insoluble in water and bases. It is soluble in dilute acids, ammonia , ammonium salt solutions and sodium cyanide solution . When heated vigorously in an oxygen atmosphere, it converts into the crystalline cadmium oxide. This is dark red, but when heated the color changes to black.
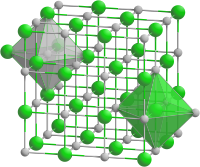
Cadmium oxide crystallizes in the cubic crystal system in the space group Fm 3 m (space group no. 225) with the lattice parameter a = 4.695 Å and four formula units per unit cell. The structure thus corresponds to the sodium chloride structure . Like zinc oxide, cadmium oxide is a non-stoichiometric oxide in which there is a slight deficiency of oxide ions compared to cadmium ions. In contrast to zinc oxide, in which additional zinc ions are present in tetrahedral interstitial spaces, this is caused by defects in the oxide lattice. The typical color change is also caused by the different number of imperfections depending on the temperature.
Cadmium oxide is a II-VI compound semiconductor with a low specific resistance for a salt of 5.5 · 10 −3 Ω · cm at 0 ° C and a band gap of 2.16 eV.
use
Cadmium oxide is used as a glass additive for tempered glasses, special colored glasses that only take on their color after tempering (heat treatment), and as a hydrogenation and dehydrogenation catalyst in synthetic organic chemistry. Alloyed with silver, it protects the surface of highly stressed electrical relay contacts .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on cadmium oxide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c Günter Hommel: Handbook of dangerous goods. Vol. 3 Leaflets 803-1205, 3rd edition, Springer, 1999, ISBN 978-3-5406-6592-2 , sheet 826 ( limited preview in the Google book search).
- ↑ Entry on cadmium oxide in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Entry in the SVHC list of the European Chemicals Agency , accessed on July 17, 2014.
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 1306-19-0 or cadmium oxide ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ a b Monteponit in: Anthony et al .: Handbook of Mineralogy , 1990, 1, 101 ( pdf ).
- ^ A b c Karl-Heinz Schulte-Schrepping, Magnus Piscator: Cadmium and Cadmium compounds . In: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2002, doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a04_499 .
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , p. 1492.
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , p. 1764.
- ↑ PH Jefferson, SA Hatfield, TD Veal, PDC King, CF McConville, J. Zúñiga – Pérez, V. Muñoz – Sanjosé: Bandgap and effective mass of epitaxial cadmium oxide. In: Appl. Phys. Lett . 92, p. 022101, doi : 10.1063 / 1.2833269 .




