Carbophenothione
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
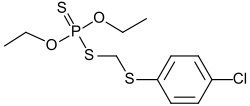
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Carbophenothione | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 11 H 16 ClO 2 PS 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 342.87 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.285 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
130 ° C (1.3 mbar) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (<40 mg l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Carbophenothione is a chemical compound from the group of thiophosphoric acid esters . The high acute toxicity led to several mass poisonings in birds.
Extraction and presentation
Carbophenothione can be obtained by reacting 4-chlorothiophenol with hydrogen chloride and formaldehyde and then with DEPA .
use
Carbophenothion is used as a universal insecticide e.g. B. for seed dressing , but mainly used in the cultivation of citrus fruits . Stauffer Chemical introduced the compound in the 1960s.
Admission
Carbophenothion was approved in Germany from 1971 to 1974.
No plant protection products containing this active ingredient are permitted in the EU or Switzerland .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on carbophenothione in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on carbophenothion in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ George A. Hamilton, Kenneth Hunter, Alexander S. Ritchie, Alexander D. Ruthven, Peter M. Brown, Peter I. Stanley: Poisoning of wild geese by carbophenothion-treated winter wheat . In: Pesticide Science . tape 7 , no. 2 , April 1976, p. 175-183 , doi : 10.1002 / ps.2780070212 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 345 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Joint Meeting on Pesticide Residues (JMPR), Monograph for Carbophenothione , accessed December 9, 2014.
- ^ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on carbophenothione in the EU pesticide database ; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on March 26, 2016.
- ↑ Regulation (EC) No. 2076/2002 of the Commission of November 20, 2002 (PDF) extending the deadline according to Article 8 (2) of Council Directive 91/414 / EEC and on the non-inclusion of certain active substances in Annex I of this Directive and the revocation of the approval of plant protection products with these active substances.

