Cystathionine β synthase
| Cystathionine β synthase | ||
|---|---|---|

|
||
| Tertiary structure of human cystathionine β synthase according to PDB 1JBQ | ||
| other names |
|
|
|
Existing structure data : 1JBQ , 1M54 , 4COO , 4L0D , 4L27 , 4L28 , 4L3V , 4PCU , 4UUU |
||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 551 amino acids , 60587 Da (isoform 1)
565 amino acids, 61863 Da (isoform 2) |
|
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Homodimer | |
| Cofactor | Pyridoxal phosphate, heme | |
| Isoforms | 2 | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene names | CBS HIP4 | |
| External IDs |
|
|
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 4.2.1.22 , lyase | |
| Response type | Transsulfurization | |
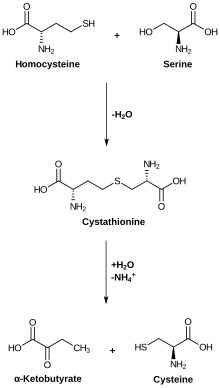
| Substrate | Homocysteine, serine | |
| Products | Cystathionine, water | |
| Orthologue | ||
| human | House mouse | |
| Entrez | 875 | 12411 |
| Ensemble | ENSG00000160200 | ENSMUSG00000024039 |
| UniProt | P35520 | Q91WT9 |
| Refseq (mRNA) | NM_000071 | NM_001271353 |
| Refseq (protein) | NP_000062 | NP_001258282 |
| Gene locus | Chr 21: 6.44 - 6.47 Mb | Chr 17: 31.61 - 31.64 Mb |
| PubMed search | 875 |
12411
|
The cystathionine β- synthase ( CBS ) is an enzyme from the group of lyases that in the transfer of sulfur-containing molecules ( transsulfuration ) in the amino acid metabolism is involved.
properties
The cystathionine-β-synthase catalyzes the coupling of homocysteine to serine , whereby cystathionine is formed with the loss of a water molecule . As a co-factor is pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) and heme used. Cystathionine-β-synthase is activated allosterically by S-adenosylmethionine . It contains an active center and two CBS domains of protein domains. A restricted function of the CBS leads to cysteinuria and homocysteinuria and an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases . Mutations in the CBS gene are associated with homocysteinuria. In animals, the CBS is mainly produced in the liver . The T833C mutation is associated with an increased risk of stroke . The gene expression of the CBS is initiated by the transcription factor farnesoid X receptor . CBS is overexpressed in some tumor cells .
The cystathionine-β-synthase belongs to the L-serine hydrolyases . Originally, a methylcysteine synthase was classified with the EC number EC 4.2.1.23 in 1961 . However, this was a side reaction of cystathionine β synthase, which is why the EC number in 1972 was deleted.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e B. Renga: Hydrogen sulfide generation in mammals: the molecular biology of cystathionine-β-synthase (CBS) and cystathionine-γ-lyase (CSE). In: Inflammation & allergy drug targets. Volume 10, Number 2, April 2011, pp. 85-91, PMID 21275900 .
- ↑ Janosík M, Kery V, Gaustadnes M, Maclean KN, Kraus JP: Regulation of human cystathionine beta-synthase by S-adenosyl-L-methionine: evidence for two catalytically active conformations involving an autoinhibitory domain in the C-terminal region . In: Biochemistry . 40, No. 35, September 2001, pp. 10625-33. doi : 10.1021 / bi010711p . PMID 11524006 .
- ↑ M. Dziegelewska, S. Holtze, C. Vole, U. Wachter, U. Menzel, M. Morhart, M. Groth, K. Szafranski, A. Sahm, C. Sponholz, P. Dammann, K. Huse, T. Hildebrandt, M. Platzer: Low sulfide levels and a high degree of cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) activation by S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) in the long-lived naked mole-rat. In: Redox biology. [Electronic publication before printing] January 2016, doi : 10.1016 / j.redox.2016.01.008 , PMID 26803480 .
- ^ R. Ding, S. Lin, D. Chen: The association of cystathionine β synthase (CBS) T833C polymorphism and the risk of stroke: a meta-analysis. In: Journal of the neurological sciences. Volume 312, number 1–2, January 2012, pp. 26–30, doi : 10.1016 / j.jns.2011.08.029 , PMID 21917271 .
- ↑ MR Hellmich, C. Coletta, C. Chao, C. Szabo: The therapeutic potential of cystathionine β-synthetase / hydrogen sulfide inhibition in cancer. In: Antioxidants & redox signaling. Volume 22, number 5, February 2015, pp. 424–448, doi : 10.1089 / ars.2014.5933 , PMID 24730679 , PMC 4307161 (free full text).
- ↑ IUBMB: EC 4.2.1.23