Dicyclohexylamine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
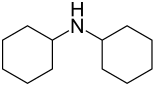
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Dicyclohexylamine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 23 N | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with an amine-like odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 181.32 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.91 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
0 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
256 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.04 hPa (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.484 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Dicyclohexylamine is a chemical compound from the group of aliphatic amines .
Extraction and presentation
Dicyclohexylamine can be prepared from cyclohexanone by hydrogenating amination or, in higher yields, from cyclohexanone and cyclohexylamine using palladium-carbon catalysts at a hydrogen pressure of 0.4 MPa. It can also be produced from phenol by means of hydrogenating amination or from phenol and aniline under appropriate conditions and with the use of catalysts. Dicyclohexylamine is also formed as a by-product in the production of cyclohexylamine from aniline and cyclohexanol or cyclohexanone.
properties
Dicyclohexylamine is a colorless liquid with an amine-like odor, which is miscible with almost all common solvents. Its aqueous solution has an alkaline reaction. From a temperature of 256 ° C the compound decomposes, producing carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
use
Dicyclohexylamine is used as an intermediate in the manufacture of oil additives , insecticides , emulsifiers , anti-corrosion agents , plasticizers , vulcanization accelerators and dyes .
The carbonate and nitrite are used as volatile corrosion inhibitors .
safety instructions
The vapors of dicyclohexylamine can form an explosive mixture with air ( flash point 99 ° C). Contact with nitrosating agents (e.g. nitrites, nitrous acid , nitrous gases) can lead to the formation of carcinogenic nitrosamines , although dicyclohexylnitrosamine has no carcinogenic effect.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k Entry on dicyclohexylamine in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Toxicological assessment of dicyclohexylamine (PDF) at the professional association for raw materials and chemical industry (BG RCI), accessed on August 22, 2012.
- ↑ Dicyclohexylamine data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 24, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on dicyclohexylamine in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Entry on VPI. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 6, 2016.
- ↑ BAUA: Dicyclohexylnitrosamine (PDF; 13 kB)


