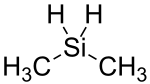
Dimethylsilane
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Dimethylsilane | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 8 Si | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless gas with a disgusting, sweet smell |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 60.17 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
gaseous |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−150.2 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
−19.6 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
hydrolyzed in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Dimethylsilane is a chemical compound from the group of organosilicon compounds .
Extraction and presentation
Dimethylsilane can be produced in quantitative yield by reacting dichlorosilane with an excess of gaseous dimethylzinc .
It can also be obtained by reducing dichlorodimethylsilane with a suitable reducing agent (e.g. lithium aluminum hydride ).
properties
Dimethylsilane is an extremely flammable, colorless gas with a flash point ≤ −30 ° C and an ignition temperature of 205 ° C. It is heavier than air ( relative gas density = 2.11), forms explosive mixtures with air (lower explosion limit at 1.2 vol.% Or 30 g · m -3 , upper explosion limit at 74 vol.% Or 1851 g · m -3 ) and can self-ignite when exposed to air.
It hydrolyzes in water or acids to form dimethylsilanediol and hydrogen, which often ignites immediately. When the liquid flows out or when large amounts of gas escape, cold mists form and spread across the floor.
use
As a precursor molecule, dimethylsilane can be used as a silicon source for the deposition of silicon-containing layers by means of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) , which are required in the manufacture of products in the electronics and photovoltaic industry, e.g. B. for low-k dielectrics .
Related links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Entry for CAS no. 1111-74-6 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 2, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ^ Alfred Stock, Carl Somieski: Siliciumwasserstoffe VI .: Chlorination and methylation of the monosilane . In: Reports of the German Chemical Society (A and B Series) . tape 52 , no. 4 , April 12, 1919, p. 695 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.19190520410 .
- ↑ Air Liquide Gas Encyclopedia: Dimethylsilane ( Memento of July 8, 2012 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Qingguo Wu, Karen K. Gleason: Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition of low-k dielectric films using methylsilane, dimethylsilane, and trimethylsilane precursors . In: Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A . tape 21 , no. 2 , March 2003, p. 388-393 , doi : 10.1116 / 1.1539086 .


![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {SiCl_ {2} H_ {2} + \ 2 \ Zn (CH_ {3}) _ {2} \ {\ xrightarrow [{}] {}} \ Si (CH_ {3}) _ { 2} H_ {2} \ + \ 2 \ ClZnCH_ {3}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f17cce77258ae89424e48a0b9b2547287df4a673)