Dinickel boride
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
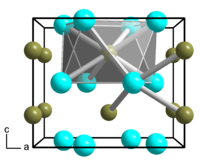
__ Ni __ B metal-metal bonds are not shown |
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Dinickel boride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | Ni 2 B | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
gray solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 128.19 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
7.9 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
1230 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water and most organic solvents |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Dinickel boride is an inorganic chemical compound of nickel from the group of borides . Other less common nickel borides are NiB, Ni 3 B, o-Ni 4 B 3 , m-Ni 4 B 3 and Ni 7 B 3 .
Extraction and presentation
Dinickel boride can be obtained by reacting nickel (II) acetate with sodium borohydride in ethanol. Nickel borides have been generally known since the first third of the last century. The representation took place by means of classical, solid-chemical synthesis routes at high temperatures (from 700 to approx. 2500 ° C) from the elements. Crystalline powders or single crystals are obtained at these temperatures.
properties
Dinickel boride is a gray solid. It has a tetragonal crystal structure with the space group I 4 / mcm (space group no. 140) and the lattice parameters a = 4.99 Å and c = 4.24 Å. In the crystal structure, which corresponds to the Cu 2 Al type, each boron atom is square-antiprismatic surrounded by eight nickel atoms, each nickel atom tetragonal-pyramidal by four boron atoms.
use
Dinickelborid is as a selective hydrogenation catalyst (eg. B. for desulfurization ), for the reduction of nitro and other functional groups, as Dehalogenierungskatalysator and as a hydrogenolysis catalyst used. It is also a component of alloys and is used to coat metals and ceramics.
Related links
- NiB : silver-gray to green solid, density 7.39 g / cm 3 , melting point 1080 ° C, space group Cmcm (space group no. 63) , CAS number: 12007-00-0
- Ni 3 B : density 8.17 g / cm 3 , melting point 1155 ° C, space group Pnma (space group no.62 ) , CAS number: 12007-02-2
- Ni 4 B 3 : space group Pnma (space group no.62 ) (density 7.57 g / cm 3 ) or space group C 2 / c (space group no.15 ) (density 7.42 g / cm 3 )
- Ni 7 B 3 : only stable between 300 and 424 ° C, space group P 6 3 mc (space group no.186)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on dinickel boride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 23, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Dale L. Perry: Handbook of Inorganic Compounds, Second Edition . CRC Press, 2016, ISBN 978-1-4398-1462-8 , pp. 288 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ A b c Thomas J. Caggiano, Sylvain Taillemaud: Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis . John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2001, ISBN 978-0-470-84289-8 , Nickel Boride.
- ↑ a b Kathrin Hofmann, Nalan Kalyon, Christine Kapfenberger, Leo Lamontagne, Salman Zarrini, Robert Berger, Ram Seshadri, Barbara Albert: Metastable Ni7B3: A New Paramagnetic Boride from Solution Chemistry, Its Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties. In: Inorganic Chemistry. 54, 2015, p. 10873, doi : 10.1021 / acs.inorgchem.5b01929 .
- ↑ a b Universität Hamburg: Dissertation by Christine Kapfenberger Synthesis and characterization of nano-scale nickel borides ( Memento from June 12, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) , December 2005, urn : nbn: de: gbv: 18-27867 , accessed on July 3 2016
- ^ A b c Joseph R. Davis: Nickel, Cobalt, and Their Alloys . ASM International, 2000, ISBN 978-0-87170-685-0 , pp. 332 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ NV Chandra Shekar, M. Sekar, P.Ch. Sahu: Equation of state and compressibility of nickel semiboride. In: Physica B: Condensed Matter. 443, 2014, p. 95, doi : 10.1016 / j.physb.2014.03.015 .
- ↑ MH Rei, LL Sheu, YZ Chen: Nickel boride catalysts in organic synthesis. I: A new ferromagnetic catalyst from the diborane reduction of nickel acetate. In: Applied Catalysis. 23, 1986, p. 281, doi : 10.1016 / S0166-9834 (00) 81298-1 .
- ↑ Entry on nickel borides. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 3, 2016.


