Dodemorph
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
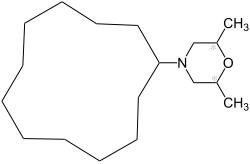
|
||||||||||||||||
| Mixture of three stereoisomers | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Dodemorph | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 35 NO | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
crystalline powder |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 281.48 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.93 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
71 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
315 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (0.0011 g l −1 ) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Dodemorph is a plant protection product from the morpholine group .
History and use
Dodemorph was discovered at BASF in 1965 and launched as a fungicide in 1971 . Dodemorph is the first morpholine fungicide to be commercialized and thus also the first sterol biosynthesis inhibitor. It is used in particular against powdery mildew . Dodemorph acts as an inhibitor of sterol-Δ8 / 7-isomerase and sterol-Δ14-reductase in ergosterol biosynthesis .
Extraction and presentation
Dodemorph can be obtained by reacting cyclododecylamine with propylene oxide and sulfuric acid.
Stereochemistry
Chemically, dodemorph is a mixture of three stereoisomers :
- meso connection,
- ( R , R ) -isomer and
- ( S , S ) -isomer,
where the ( R , R ) -isomer and the ( S , S ) -isomer form a racemate , ie represent a 1: 1 mixture. This mixture is also called the trans isomer.
Admission
In 2008, the EU Commission included Dodemorph in the list of active ingredients in pesticides, restricting it to “use as a fungicide on ornamental plants in greenhouses” .
In Austria and Switzerland it is no longer approved as a plant protection product, but it is in Germany.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Günter Hommel (Ed.): Handbook of dangerous goods: Merkblätter 2072–2502 . Springer, 2004, ISBN 3-540-20370-2 , pp. 2374 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on Dodemorph in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 23, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on Dodemorph in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Dodemorph data sheet , PESTANAL at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on June 29, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ^ Clemens Lamberth, Jürgen Dinges: Bioactive Heterocyclic Compound Classes: Agrochemicals. John Wiley & Sons, 2012, ISBN 978-3-527-33396-7 , p. 119 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide synthesis handbook . 1996, ISBN 978-0-8155-1401-5 , pp. 475 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Commission Directive 2008/125 / EC of December 19, 2008 (PDF) amending Council Directive 91/414 / EEC to include aluminum phosphide, calcium phosphide, magnesium phosphide, cymoxanil, dodemorph, 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid methyl ester, metamitron, sulcotrione , Tebuconazole and triadimenol as active ingredients.
- ^ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Dodemorph in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on December 6, 2019.



