Ethylene glycol monoisopropyl ether
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
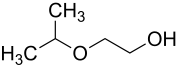
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Ethylene glycol monoisopropyl ether | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 12 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with an ethereal odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 104.152 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.90 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
<−60 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
142-144 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
5.99 h Pa (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
miscible with water |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4095 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 5 ml m −3 or 22 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
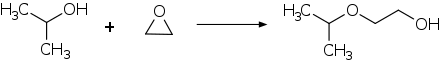
Ethylene glycol monoisopropyl ether is a monoether of ethylene glycol and belongs to the group of glycol ethers .
Presentation and extraction
Ethylene glycol monoisopropyl ether can be prepared by adding 2-propanol to ethylene oxide in the presence of boron trifluoride at 80 ° C. Alternatively, ethylene glycol can be etherified with 2-bromopropane .
properties
Physical Properties
Ethylene glycol monoisopropyl ether is a colorless liquid with an ethereal odor. The compound boils at 142 ° C. under normal pressure. The enthalpy of vaporization at the boiling point is 40.42 kJ mol −1 , under standard conditions 50.14 kJ mol −1 . According to Antoine, the vapor pressure function results from log 10 (P) = A− (B / (T + C)) (P in bar, T in K) with A = 4.70544, B = 1692.265 and C = −54.696 in the temperature range from 338.8 K to 413.8 K. The heat capacity at 25 ° C is 238.8 J · mol −1 · K −1 . The compound can be mixed with water in any proportion.
Chemical properties
The compound reacts violently with strong oxidizing agents . Incompatible combinations of substances are possible with strong bases and acids, aliphatic amines and isocyanates. The reaction with sodium cyanate gives the corresponding primary carbamate .
Safety-related parameters
Ethylene glycol monoisopropyl ether forms highly flammable mixtures with air. The flash point is 43 ° C. The explosion range is between 1.4% by volume (64 g / m 3 ) as the lower explosion limit (LEL) and 13% by volume (565 g / m 3 ) as the upper explosion limit (UEL). The ignition temperature is 240 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T3.
use
Ethylene glycol monoisopropyl ether is a versatile solvent, such as for resins and polymers with little polarity in paints and varnishes. The compound is also found in ink for inkjet printers. It has been replaced industrially by other similar solvents.
safety instructions
Ethylene glycol monoisopropyl ether is acutely and chronically harmful if inhaled or absorbed through the skin. It can also harm fertility and the unborn child.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Entry on ethylene glycol monoisopropyl ether in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 9, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-314.
- ↑ Entry on 2-isopropoxyethanol in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 109-59-1 or ethylene glycol monoisopropyl ether ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ Patent DE578722 ( IG Farben 1931)
- ↑ Whitesides, GM; Holtz, D .; Roberts, JD: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. The Effect of Structure on Magnetic Nonequivalence Due to Molecular Asymmetry in J. Am. Chem. Soc. 86 (1964) 2628-2634, doi : 10.1021 / ja01067a022 .
- ↑ a b Majer, V .; Svoboda, V .: Enthalpies of Vaporization of Organic Compounds: A Critical Review and Data Compilation in Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, 1985, 300.
- ↑ Dykyj, J .; Seprakova, M .; Maulech, J .: Physical properties of ethylene glycol and its derivatives (II) Vapor tensions of alkoxyethanols and other derivatives of ethylene glycol in Chem. Zvesti 11 (1957) 461-466.
- ↑ Kusano, K .; Suurkuusk, J .; Wadsö, I .: Thermochemistry of solutions of biochemical model compounds. 2. Alkoxyethanols and 1,2-dialkoxyethanes in water in J. Chem. Thermodyn. 5 (1973) 757-767, doi : 10.1016 / S0021-9614 (73) 80017-5 .
- ↑ Stephenson, RM: Mutual solubilities: water-glycol ethers and water-glycol esters in J. Chem. Eng. Data 38 (1993) 134-138, doi : 10.1021 / je00009a033 .
- ↑ Douheret, G .; Holczer, MB; Peyrelier, R .; Davis, MI: Speeds of Sound and Excess Volumetric Properties of Mixtures of Water with 2-Propanol and with Ethylene Glycol Monoisopropyl Ether at 298.15 K in J. Chem. Eng. Data 39 (1994) 868-872, doi : 10.1021 / je00016a053 .
- ↑ a b Pohanish, RP; Greene, SA: Wiley Guide to Chemical Incompatibilities , John Wiley and Sons Inc. 2003, ISBN 0-47 1-23859-7 .
- ↑ Modarresi-Alam, AR; Rostamizahed, M .; Najafi, P .: Solvent-Free Preparation of Primary Carbamates in Turk. J. Chem. 30 (2006) 269-276.
- ^ A b c E. Brandes, W. Möller: Safety-related parameters - Volume 1: Flammable liquids and gases , Wirtschaftsverlag NW - Verlag für neue Wissenschaft GmbH, Bremerhaven 2003.
- ↑ Stoye, D .: Solvents in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry , 2005 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a24_437 .
- ↑ Patent DE 202,004,021,559 (EI du Pont de Nemours and Company, Wilmington, Del., US, 2009)
- ↑ BASF - Solvent overview