Funar
| Funar | ||
|
||
| Data | ||
| surface | 89.73 km² | |
| population | 1,166 (2015) | |
| Chefe de Suco | Francisco Soares (election 2009) |
|
| Aldeias | Population (2015) | |
| Bamatac | 703 | |
| Fahi Lihun | 155 | |
| Lawado | 232 | |
| Maucucurian | 76 | |
|
|
||
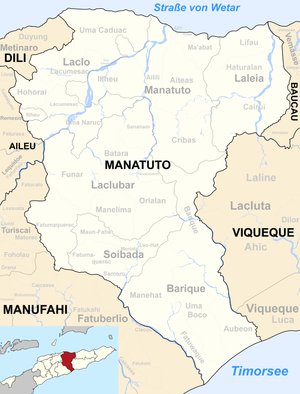
Funar is an East Timorese suco in the Laclubar administrative district ( Manatuto municipality ).
geography
| Funar | ||
| places | position | height |
| Sassahi | 8 ° 46 ′ S , 125 ° 53 ′ E | ? |
| Funar | 8 ° 45 ′ S , 125 ° 52 ′ E | ? |
Before the 2015 regional reform, Funar had an area of 91.55 km². Now there are 89.73 km². The Suco is located in the northwest of the Laclubar administrative office. To the south is the Suco Fatumaquerec , southeast of the Suco Manelima and to the east the Sucos Orlalan and Batara . In the north of Funar is the administrative office Laclo with its Suco Uma Naruc and in the west the administrative offices Remexio with the Suco Faturasa and Lequidoe with the Suco Faturilau belonging to the municipality of Aileu . The Northern Lacló flows along the border of Funar in the northwest. Most of the rivers that have their source in Funar belong to its system: the Hatobutaban , the border river in the west, the Aimaleum , the Mahonay and the Lago Coi , the border river in the east. The Buarahum , a source river of the Sáhen, flows along the southern border .
To the south is the village of Sassahi . In addition to the public facilities in Laclubar, there is also a primary school in Sassahi. A larger town west of Laclubar has a primary school ( Escola Primaria Funar ), a helipad and a medical station. Missionaries built a small Christian shrine to the Virgin Mary on a mountain in the center of Sucos, which according to the old belief is holy ( lulik ) .
The four Aldeias Bamatac , Fahi Lihun , Lawado and Maucucurian are located in the Suco . The settlements Lawado and Bamatac near the administrative capital Laclubar have been located in Suco Orlalan since the territorial reform of 2015.
Residents
1166 inhabitants live in the Suco (2015), 617 of whom are men and 549 women. The population density is 13.0 inhabitants / km². There are 168 households in the Suco. Almost 95% of the population name Idaté as their mother tongue. 2.5% speak Tetum Prasa and a minority speak Adabe .
history
In 1905 Funar was attacked by the Portuguese . The small kingdom owned a large herd of buffalo. When they refused to sell them, the scorned buyer Manuel das Neves complained to Governor José Celestino da Silva , who sent a punitive expedition against the alleged rebels. 800 Timorese warriors in Portuguese service fought for 26 days, Funar was sacked and devastated. The survivors were taken to Manatuto. Funar's territory was divided among the neighboring empires.
During the civil war in East Timor in 1975 all relic houses ( Uma Lulik ) were burned down. After the Indonesians occupied the country , the people of Funar were forcibly relocated. They were only able to return to their old homeland in the 1990s. Above all, the belief in the country's lulik was a reason for their return. According to ancient belief, the people of Funar could only be happy in the land of their ancestors.
politics
In the 2004/2005 elections , João da Cruz was elected Chefe de Suco. In the 2009 elections won Francisco Soares .
Web links
- Results of the 2010 census for the Suco Funar ( tetum ; PDF; 8.3 MB)
- Results of the 2015 census for the Suco Funar (tetum; PDF)
- Seeds of Life: Suco information sheets Laclubar (tetum)
- Pictures of the region around Funar
- Houses in Funar
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Direcção-Geral de Estatística : Results of the 2015 census , accessed on November 23, 2016.
- ↑ Fallingrain.com: Directory of Cities, Towns, and Regions in East Timor
- ↑ Direcção Nacional de Estatística: Population Distribution by Administrative Areas Volume 2 English ( Memento of the original from January 5, 2017 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (2010 census; PDF; 22.6 MB)
- ^ Timor-Leste GIS-Portal ( Memento from June 30, 2007 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ List of polling stations for the parliamentary elections in East Timor 2007 (PDF file; 118 kB)
- ↑ UNMIT map of the Manatuto district, August 2008 ( Memento of the original from December 3, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF; 581 kB)
- ^ Judith Bovensiepen, Frederico Delgado Rosa: Transformations of the sacred in East Timor , p. 35, accessed December 27, 2017.
- ↑ Jornal da Républica with the Diploma Ministerial n. 199/09 ( Memento of February 3, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) (Portuguese; PDF; 323 kB)
- ↑ Results of the 2010 census for the Suco Funar ( tetum ; PDF; 8.3 MB)
- ↑ Monika Schlicher: Portugal in East Timor. A critical examination of the Portuguese colonial history in East Timor from 1850 to 1912. Aberag, Hamburg 1996. ISBN 3-934376-08-8
- ^ Judith Bovensiepen, Frederico Delgado Rosa: Transformations of the sacred in East Timor , accessed December 27, 2017.
- ^ Judith Bovensiepen: Spiritual Landscapes of Life and Death in the Central Highlands of East Timor , Anthropological Forum, Volume 19, Number 3, November 2009, pp. 323-338 (16) , accessed December 27, 2017.
- ↑ Secretariado Técnico de Administração Eleitoral STAE: Eleições para Liderança Comunitária 2004/2005 - Resultados ( Memento of August 4, 2010 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Secretariado Técnico de Administração Eleitoral STAE: Eleições para Liderança Comunitária 2009 - Resultados ( Memento of August 4, 2010 in the Internet Archive )