Guaiaculen
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
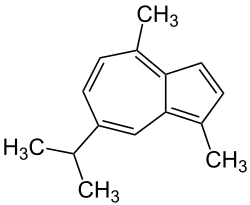
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Guaiaculen | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 18 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
dark blue crystals with a low melting point |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 198.30 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.976 g cm −3 (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
27-29 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Guaiaculene (from guaiac and French: azure "blue") or 7-isopropyl-1,4-dimethylazulene , also azulone , is a blue crystalline aromatic hydrocarbon that is used in particular in cosmetics and medicine.
properties
At approx. 600 µg / kg, guaiacol is only sparingly soluble in water. But it is soluble in ethanol , diethyl ether and ethyl acetate .
Pure guajazulene consists of blue crystals, but liquid solutions or mixtures with solid and liquid components are mainly available on the market. Guajazulen is almost odorless.
Guajazulene can have local anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects. However, whether this has any therapeutic benefit is controversial.
Occurrence
Guaiaculene is obtained either from gujaol , the essential component of the oil from Bulnesia sarmientoi and other tree species closely related to the guaiac tree, or from caryophylls , a component of clove oil .
use
Guajazulene (7-isopropyl-1,4-dimethylazulene) is often used as a substitute for chamazulene (1,4-dimethyl-7-ethylazulene), an essential component of chamomile oil , as it has very similar properties but is cheaper to manufacture.
In cosmetics , guajazulene is often a component of ointments or creams for skin care.
It is used medically both internally, against inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, the respiratory tract or the skin, and externally, against inflammation of the skin or sunburn.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Entry on guajazulene at TCI Europe, accessed on March 1, 2015.
- ↑ a b c d e f g data sheet guaiazulene, 99% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 1, 2015 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d Ernst Steinegger, Rudolf Hansel: Pharmakognosie . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-662-09267-5 , pp. 1048 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ A b William M. Haynes: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 96th Edition . CRC Press, 2015, ISBN 978-1-4822-6097-7 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ See Septimus Piesse : On the Coloring Principle of Volatile Oils . In: Chemical News . No. 8 , 1863, p. 245 ( online [accessed March 2, 2015]).
- ↑ Joel Reza, Arturo Trejo, Luz Elena Vera-Ávila: Determination of the temperature dependence of water solubilities of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a generator column-on-line solid-phase extraction-liquid chromatographic method . In: Chemosphere . No. 47 , 2002, p. 933–945 ( online [PDF; accessed March 2, 2015]).
- ^ A b c Rudolf Hansel, Joseph Hölzl: Textbook of pharmaceutical biology. Springer-Verlag, 1996, p. 75.
