Hanford Reach National Monument
| Hanford Reach National Monument | ||
|---|---|---|
| Columbia River in the reserve | ||
|
|
||
| Location: | Washington , United States | |
| Specialty: | River landscape in semi-desert | |
| Next city: | Richland , Washington | |
| Surface: | 789.1 km² | |
| Founding: | June 9, 2000 | |
Hanford Reach National Monument is a nature reserve of the type of a national monument in the south of the US state Washington . It was built in 2000 by President Bill Clinton and currently consists of the former security zone around Hanford Site , a decommissioned nuclear facility belonging to the Department of Energy , where plutonium for nuclear weapons was produced as part of the Manhattan Project from 1943 . Parts of the site are radioactive or contaminated with PCBs . As part of the ongoing dismantling of the facilities and the disposal of the nuclear waste , further decontaminated areas will be added to the protected area after their clearance.
The reserve is located on and in an approximately 80 km long loop of the Columbia River above Richland , which is the longest free-flowing section of the river. The area is under the control of the United States Fish and Wildlife Service as one of only two National Monuments and is jointly administered by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service with the Saddle Mountain National Wildlife Refuge , an adjacent wildlife sanctuary.
description
Hanford Reach is located in the Columbia Basin , a plain between the Cascade Range and the Rocky Mountains . At the end of the Miocene and the beginning of the Pliocene , about 5.33 million years ago, huge basalt flows of volcanic origin created the plain, which today is defined by a semi-arid climate and steppe vegetation .
The sparse vegetation is characterized by a plant community of couch grass and sagebrush . This also includes various bluegrass . There are willow bushes by the river . The protected area preserves the almost undisturbed fauna of the large ecosystem. Around 240 species of birds , 1,500 insect species , 43 mammals , including nine species of bats and 43 species of fish have been identified in the area. After the military reactors were shut down until 1991, the introduction of heated cooling water into the river was greatly reduced and the fish populations recovered within a few years. Today around 80% of the king salmon spawn in the upper Columbia River system in the sanctuary.
The river bend and the adjacent chain of hills Rattlesnake Mountains and Wahluke Slope were inhabited by Indians in prehistoric times and also after contact with the whites . The oldest traces are stone tools of the Paleo-Indians around 10,000 years ago, in the 19th century the Wayampam , Yakama , Colville , Umatilla and Nez Percé lived, hunted and fished on and around the river. There are over 150 identified archaeological sites in the area, only a few have been excavated so far. The first whites in the area were the participants of the Lewis and Clark Expedition in 1805. Around 1860 a ferry was set up across the river in the north of what is now the protected area. It was not until 1870 that significant numbers of white people settled in the area and founded the two places Hanford and White Bluffs , the settlement remained sparse. In December 1942, just days after the first controlled nuclear chain reaction by Enrico Fermi , the federal government selected the area as the location for nuclear weapons production; the approximately 1500 families living in the area sold voluntarily or were expropriated, compensated and relocated.
The nuclear weapons production at Hanford Site was subject to the strictest safety regulations. A zone of at least six miles (approximately 10 km) in each direction from the facilities was a restricted area and was deserted. There had been no human interference there since nuclear weapons production began in 1943.
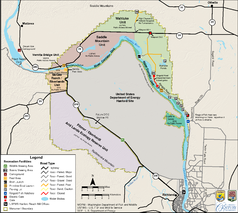
The National Monument
Due to the special history of the area and the wilderness character of the former restricted area, parts of the national monument are designated as priority area for ecological research according to protected area category 1 of the IUCN World Conservation Organization , they are not accessible to visitors.
- Columbia River Corridor : River and bank areas are freely accessible, camping is not permitted.
- Fitzner-Eberhardt Arid Lands Ecology Reserve : priority area for ecological research, closed to the public.
- Saddle Mountain Unit : priority area for ecological research, closed to the public.
- McGee Ranch and Riverlands : Still used by the Department of Energy, approval awaited
- Vernita Bridge : open to the public
- Wahluke Slope : open to the public
The area does not yet have a visitor center. Information and maps are available from the Fish and Wildlife Service office in Richland.
Web links
- US Fish and Wildlife Service: Hanford Reach National Monument (official website, English)
- US Department of Energy: Hanford Site (official website, English)
- Entry in the Washington encyclopedia HistoryLink (English)