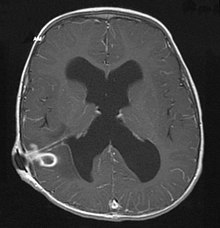
Herd encephalitis
A brain abscess is an at least one location (lat. Focus occurring = cooker) inflammation of the brain . This is mostly caused by bacteria , more rarely by fungi or other pathogens and is therefore also known as septic herd encephalitis.
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| G04.2 | Bacterial meningoencephalitis and meningomyelitis, not elsewhere classified |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
Emergence
For herd encephalitis to develop, pathogens have to get into the brain. There are different ways to do this:
- direct introduction of germs through open traumatic brain injury (TBI)
- based on propagated inflammation ( sinusitis , mastoiditis ) or from the tooth (odontogenic)
- Inundation with the blood (septic herd encephalitis, see below)
- by infection of an implant (liquor drainage)
The risk increases with a weakening of the immunity , which can be caused by congenital or acquired factors ( multiple trauma , acute infectious disease , tumor , AIDS ).
to form
Brain abscess
The body's own defense ( immunity ) leads to a melting of the highly infected tissue and to the separation from the surrounding tissue. This creates an abscess . This process leads to an increase in volume (mass), which, due to the bony cranial cavity, can quickly lead to an increase in pressure with serious complications (e.g. entrapment ). In the case of a brain abscess, four stages are distinguished using computed tomography:
- early "cerebritis" (inflammation of the brain): indistinctly delimited hypodensity
- late “cerebritis”: hypodensity with a central, sharply delimited ring-shaped contrast enhancement
- early capsule formation
- late capsule formation: visible as weak hyperdensity with central hypodensity even without contrast agent administration.
Septic embolic herd encephalitis
The spread of infected thrombi leads to a combination of ischemic stroke and simultaneous inflammation. The course is often unfavorable due to the infection of the brain tissue that is no longer supplied with blood (only minimal immunity there due to a lack of blood circulation) and bleeding into the infarct in many cases.
The starting point is almost always a bacterial inflammation of the inner wall of the heart ( endocardium ) and especially the heart valves there ( endocarditis ).
Septic metastatic herd encephalitis
If bacteria occur in the flowing blood (septicemia), the pathogen can spread into the brain. This is only possible in the context of a severe general inflammatory disease or mostly sepsis . Further development is mainly determined by the underlying infection.
Diagnosis
First of all, an imaging examination is required, which is usually carried out using contrast-enhanced computed tomography or magnetic resonance tomography . In most cases, the inflammatory focus , the surrounding edema and an accumulation of the contrast medium can be seen here.
Finally, the detection of the pathogen is of great importance for further therapy . This is due to microbiological tests of cerebrospinal fluid (see spinal tap ) or blood cultures or possible of the oven (after neurosurgical rehabilitation or at least puncture ) is possible. In addition to knowledge of the pathogen, its sensitivity to drugs ( antibiogram ) is also important.
Then, if necessary, the origin of the pathogen must be sought (the oral cavity, mastoiditis, sinusitis, otitis, endocarditis come into consideration). This often requires computed tomography of the chest and abdomen (with a contrast medium) or the paranasal sinuses . Echocardiography is also very important.
therapy
Hearth remediation
Wherever possible, the inflammatory focus should be removed by surgery. For this is neurosurgery responsible.
However, this procedure is not always possible, e.g. B. if the focus is on a particularly important brain region (e.g. language center or brain stem ). Then only drug treatment (see below) is possible, which may then have to take longer.
Antibiotics
After obtaining material for the microbiological examination (see above), treatment with antibiotics is necessary even if herd encephalitis is suspected . The treatment is initially carried out with a broad spectrum of activity (e.g. 3rd generation cephalosporin + staphylococcal penicillin). After determining the antibiogram, you can switch to targeted therapy (usually with a less broad spectrum).
In special cases, antibiotics are also administered intrathecally .
If an infection with fungi is suspected, an additional antifungal agent (e.g. amphotericin B) must be treated accordingly.
Treatment of the underlying disease
Depending on the starting point of the infection, the treatment of the underlying disease must not be missed. This primary focus must be surgically repaired immediately, especially in the case of a cerebral abscess spread from the ear or paranasal sinus. With endocarditis , for. B. the insertion of an artificial heart valve may be necessary. Other foci of pus (e.g. infected wounds, tooth root abscess, osteomyelitis, etc.) should be surgically cleaned up if possible.
Treatment of sepsis is usually only possible in an intensive care unit .
Complications
The most common complication is the mass with increased intracranial pressure . Neurosurgical interventions may be necessary again, in particular liquor drainage or, in individual cases, a craniectomy .
Further complications are inflammation of the vessel walls (vasculitis) and cerebral infarction, both from vascular occlusion and from bleeding.
forecast
The further development of the patient first depends on the patient's requirements:
- General condition (age, previous illnesses, etc.)
- Underlying disease ( endocarditis , TBI )
- Comorbidities ( diabetes mellitus , AIDS , etc.)
However, these can hardly be influenced.
Medical care is also important:
- Availability of specializations (radiology, neurology, neurosurgery, intensive therapy)
- Availability of diagnostics (laboratory, computed tomography, microbiology)
- early start of consistent treatment (antibiotics and surgery)
These factors can be influenced; admission to a suitable hospital can be decisive.
literature
- Hilmar Prange, Andreas Bitsch: Neurological intensive care medicine. Thieme 2004. ISBN 3-13-129821-9
- Manfred Stöhr, Thomas Brandt, Karl M. Einhäupl: Neurological Syndromes in Intensive Care Medicine. Kohlhammer 1998. ISBN 3-17-014557-6
- R. Nau et al .: Brain abscess. Guidelines of the German Society for Neurology. Working Group of Scientific Medical Societies , 2008.
Web links
- Guideline for bacterial (purulent) meningoencephalitis of the German Society for Neurology . In: AWMF online (as of 10/2005)
- Guideline atypical pathogen-related meningoencephalitis of the German Society for Neurology . In: AWMF online (as of 10/2005)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Alphabetical directory for the ICD-10-WHO version 2019, volume 3. German Institute for Medical Documentation and Information (DIMDI), Cologne, 2019, pp. 221 + 554
- ^ Marianne Abele-Horn: Antimicrobial Therapy. Decision support for the treatment and prophylaxis of infectious diseases. With the collaboration of Werner Heinz, Hartwig Klinker, Johann Schurz and August Stich, 2nd, revised and expanded edition. Peter Wiehl, Marburg 2009, ISBN 978-3-927219-14-4 , pp. 68-72 ( brain abscess ).
- ↑ Marianne Abele-Horn (2009), p. 69.
- ↑ Marianne Abele-Horn (2009), p. 72 ( intraventricular therapy ).