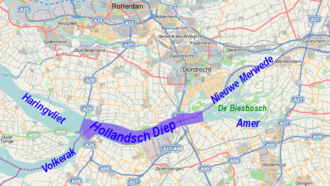
Hollands Diep
Located in the Netherlands , Hollands Diep , also Hollandsch Diep ( German Dutch depth ), is a broad, west-facing arm of the river in the course of the southern of the two main estuaries of the Rhine . The Hollands Diep was an open bay in the North Sea until 1970 . Due to the construction of the Haringvlietdam as part of the Delta Works , access from the sea is only possible via locks.
Location and characteristics
The approximately 21 kilometers long inland waterway near the coast is the penultimate section of the widest arm of the Rhine in the branching Rhine-Maas delta . It begins in the east as a continuation of the Neue Merwede , in turn the continuation of the Waal (main strand of the Rhine). The Amer , which is the lowest section of the Meuse ( Bergsche Maas ), flows out at this point . The partially natural delta landscape of the Biesbosch lies in the corner of the mouth .
At its western end, the estuary-like widened Hollands Diep forks into the two waters of Volkerak in the southwest (separated by locks) and Haringvliet in the west. Both, and thus Hollands Diep, were dammed from the North Sea when the Delta Works were built . As a result, all of these waters have been transformed from salty or brackish estuaries under the influence of tides into freshwater lakes since 1970 . The cautious renewed cracking, which has been ongoing since 2010, only affects the western part of the neighboring Haringvliet.
Hollands Diep is located on the border between the Dutch provinces of Zuid-Holland in the north and Noord-Brabant in the south. In the north of Hollands Diep lies the Hoeksche Waard and Dordrecht Island; between them, the Dordtse Kil creates a connection to the Old Meuse and the Nieuwe Waterweg .
Emergence
The storm surge of 1216 left a gap in the coastal dunes near Voorne , which initially created the neighboring Haringvliet (name since 1315). Around 1250 the water reached the strait , from where it found its way as far as Brabant. The Hollands Diep was created in 1421 by the so-called Elisabethenflut , which fundamentally changed the estuaries of the Rhine, Meuse and Scheldt. At the beginning, the new bay was many times wider and extended many kilometers to the east. The Hollands Diep shrank to its present-day size due to landings , silting up and poldering . The Hollands Diep was formerly called Wijvekeen .
Hydrological aspects
Since 1904 the old confluence of the Maas into the Waal was closed ( Afgedamde Maas ) in Hollandsch Diep the water of the Maas ( Bergsche Maas ) unites with more than half of the Rhine water (by the Nieuwe Merwede created in 1874 ). Until 1970, the discharge from here into the sea was largely distributed between the Haringvliet and the Volkerak , which at that time still had several drainage routes. The Volkerak has been separated from the delta since 1970. On average, 80% of the water from Hollands Diep reaches the sea through the mouth of the Haringvliet, and on average one fifth is branched off through the Spui into the Nieuwe Waterweg .
The water management in the Rhine delta aims at a flow rate of around 1500 m³ / s in the Nieuwe Waterweg (through the port of Rotterdam ) by means of several barrages ; the water that goes beyond this, especially the Waal , is mainly diverted via the Nieuwe Merwede and the Hollands Diep; on average this is around 950 m³ / s. Conversely, when the water level in the Rhine is low (less than 1100 m³ / s at the Lobith gauge on the German border), the Haringvliet dam is almost closed, so that the combined water from the Waal and Maas flows into the Nieuwe Waterweg via different routes. As a result, the Hollands Diep, together with the Nieuwe Merwede and the Haringvliet, have an extremely seasonal flow with fluctuations in level of almost two meters.
There are also daily fluctuations, known as the apparent tide , which result from the closing of the Haringvliet locks at high tide.
Cultural landscape and history
Before 1872, the Hollands Diep could only be crossed with difficulty by ship. It was thus also a symbol of the previously important cultural gap between the Protestant north and the Catholic south of the Netherlands. The Dutch idioms boven Moerdijk ("above Moerdijks") or beneden Moerdijk ("below Moerdijks") want to say "in actual, Protestant Holland" or "in the southern, Catholic Netherlands" (North Brabant and Limburg ).
The historic fortress town of Willemstad (part of the fortifications on Hollands Diep and Volkerak ) is located on the south bank .
Infrastructure
About the Hollands Diep in lead Moerdijk the Moerdijkbruggen (a highway and two railway bridges). At the transition to the other estuaries are the Haringvlietbrug and the Helegatdam with locks .
Part of the Hollands Diep is part of the shipping route between Rotterdam and Antwerp . The port facilities at Moerdijk-Zevenbergen on the south bank also bear witness to this .
Web links
- Hollandsch Diep . In: rijkswaterstaat.nl . Rijkswaterstaat (Dutch)
- Information film by the Rijkswaterstaat about keeping the Haringvliet barrage wide open YouTube (Dutch, German subtitles)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Note: This value from the publications of the Rijkswaterstaat, together with the runoff from the Nieuwe Waterweg, exceeds the mean water flow of the Rhine at the German-Dutch border of 1300 m³ / s. See: the Rhine river system
- ^ Rijkswaterstaat: Water Management in the Netherlands, 2011