Hydrogen selenide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
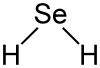
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Hydrogen selenide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | H 2 Se | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless gas with an unpleasant odor of rotten radish |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 80.98 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
gaseous |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−66 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
−41.4 ° C (decomposition above 150 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.91 M Pa at 20 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
poor in water (9.8 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.412 (16.85 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
|
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Hydrogen selenide , also known as monoselan , is a combination of selenium and hydrogen . It arises when salt-like selenides are dissolved in dilute acids. Hydrogen selenide is a colorless, extremely toxic gas with an unpleasant foul odor. Even a single inhalation of small amounts leads to unpleasant, long-lasting irritation of the mucous membranes (so-called "selenium fever"). Hydrogen selenide is more toxic than hydrogen sulfide . In laboratory tests that produce only very small amounts of hydrogen selenide, it is essential to work under a fume cupboard and to wear a gas-tight protective suit.
Hydrogen selenide is used in the semiconductor and electronics industry for doping of semiconductors .
Physical Properties
Hydrogen selenide is angled (bond angle 91 °), the bond length Se – H is 146 pm.
| property | value |
|---|---|
| Critical temperature | 138 ° C |
| Critical pressure | 8.92 M Pa |
| Critical density | 0.76 kg / l |
| Triple point temperature | −65.65 ° C |
| Triple point pressure | 0.2738 bar |
Chemical properties
Compared to hydrogen sulfide, hydrogen selenide is a stronger reducing agent. Aqueous solutions of hydrogen selenium react with atmospheric oxygen, causing red selenium to precipitate.
Manufacturing
In the laboratory, pure hydrogen selenide is obtained by dissolving dry aluminum selenide in water, or by reacting the elements at 400 ° C:
use
By reaction with a Kaliumantimonyltartratlösung can antimony (III) selenide can be produced.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i entry to hydrogen selenide in the GESTIS database of IFA , retrieved on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ PG Sennikov, VE Shkrunin, DA Raldugin, KG Tokhadze: Weak Hydrogen Bonding in Ethanol and Water Solutions of Liquid Volatile Inorganic Hydrides of Group IV-VI Elements (SiH 4 , GeH 4 , PH 3 , AsH 3 , H 2 S, and H 2 Se). 1. IR Spectroscopy of H Bonding in Ethanol Solutions in Hydrides . In: The Journal of Physical Chemistry . tape 100 , no. January 16 , 1996, ISSN 0022-3654 , pp. 6415-6420 , doi : 10.1021 / jp953245k .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 7783-07-5 or hydrogen selenium ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ Limit values for working materials ( Memento of the original from September 23, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Ordinance of the Federal Minister for Labor, Social Affairs and Consumer Protection (Limit Values Ordinance GKV 2011), Austria.
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , p. 627.
- ↑ a b Entry on hydrogen selenide. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 25, 2014.
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 91st – 100th, improved and greatly expanded edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1985, ISBN 3-11-007511-3 , p. 528.
- ↑ G. Brauer (ed.), Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry 2nd ed., Volume 1, Academic Press 1963, pp. 418-419.
- ^ Dale L. Perry: Handbook of Inorganic Compounds, Second Edition . Taylor & Francis US, 2011, ISBN 1-4398-1462-7 , pp. 39 ( limited preview in Google Book search).






