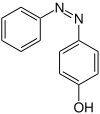
Hydroxyazobenzenes
| Hydroxyazophenols | ||||||
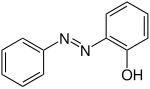
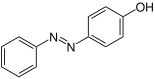
| Surname | 2-hydroxyazobenzene | 3-hydroxyazobenzene | 4-hydroxyazobenzene | |||
| other names | o -hydroxyazobenzene | m -hydroxyazobenzene | p -hydroxyazobenzene | |||
|
Structural formula above: ( E ) -isomer below: ( Z ) -isomer |
|

|
|
|||
| CAS number |
|
|
|
|||
| PubChem | 6506404 | 15723297 | 5354198 | |||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 10 N 2 O | |||||
| Molar mass | 198.22 g mol −1 | |||||
| Physical state | firmly | |||||
| Melting point | 83 ° C | 114-115 ° C | 157.5-159.5 ° C | |||
| boiling point | 230 ° C | |||||
| solubility | practically insoluble in water , good in diethyl ether and ethanol |
|||||
|
GHS labeling |
|
|
|
|||
| H and P phrases | no H-phrases | no H-phrases | 315-319-335 | |||
| no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | ||||
| no P-phrases | no P-phrases | 261-305-338-351 | ||||
Hydroxyazobenzenes are organic compounds from the group of azobenzenes . They also belong to the azo dyes . They have a characteristic azo group and two benzene rings . The hydroxy group on one of the benzene rings acts as a substituent . Theoretically, three constitutional isomers with the empirical formula C 12 H 10 N 2 O are possible, each of which occurs in two ( E , Z ) isomers .
presentation
Hydroxyazobenzenes can be prepared from diazonium salts and phenols or aromatic amines by coupling reactions . They are also the product of the Gelding rearrangement . In this case, azoxybenzenes react in an acidic environment to form hydroxyazobenzenes, more precisely to p- hydroxyazobenzene. O -hydroxyazobenzene is formed in addition to p -hydroxyazobenzene when benzene diazonium chloride is coupled with phenol. The product contains only at most 1% of the ortho - isomer . This can be separated from the less volatile para isomer by steam distillation . In addition, the ortho connection is created when the para position is occupied.
Isomerism
In addition to structural isomers m - o - p -Hydroxyazobenzol there to each of the individual isomers another E - and Z isomer. All the information in the table below relates to the E , Z -isomer mixture, since it is difficult to separate the isomers from one another. Due to steric hindrances , the E isomers are more stable, but rearrangement into the Z isomers is possible.
The hydroxyl group on the benzene ring can increase the electron density in the benzene ring through the mesomeric effect (+ M effect). The electron-withdrawing inductive (- I ) effect is superimposed by the mesomeric effect. Because of these effects, p- hydroxyazobenzene is the most stable. The m -hydroxyazobenzene is therefore the most unstable. The o -hydroxazobenzene lies in between.
properties
The hydroxyazobenzenes are classified as highly hazardous to water ( WGK 3 ). Due to their azo group, the hydroxyazobenzenes appear colored. The p- hydroxyazobenzene has a yellowish-orange color and crystallizes in the form of prisms. The o- hydroxyazobenzene appears in an orange hue.
use
Like many other azo dyes, hydroxyazobenzenes are used to color soaps , varnishes , fats and resins .
Individual evidence
- ^ A b c Louis F. Fieser, Mary Fieser: Textbook of organic chemistry . Chemie, Weinheim 1957, p. 713 .
- ↑ a b c Gavriella Gabor, Yael F. Frei, Ernst Fischer: Tautomerism and Geometric Isomerism in Arylazophenols and Napthols IV. - Spectra and Reversible Photoreactions of m- and p-Hydroxyazobenzene , J. Phys. Chem. 72: 3266-3272 (1968).
- ↑ a b Entry on 4- (phenylazo) phenol at TCI Europe, accessed on May 7, 2014.
- ↑ a b Data sheet 4-Phenylazophenol from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 8, 2014 ( PDF ).
- ^ M. Windholz: The Merck Index . Merck & Co., Rahway 1976, ISBN 978-0-911910-26-1 , pp. ONR-92 .
- ↑ a b Dietrich Schulte-Frohlinde: About the thermal catalytic cis - trans rearrangement of substituted azobenzenes , Liebigs Ann. Chem. 612: 138-152 (1958).
- ↑ Charles E. Mortimer ; Ulrich Müller: Chemistry . Thieme, Stuttgart 2010, ISBN 978-3-13-484310-1 , p. 549-550 .
- ↑ Beyer, Walter: Textbook of organic chemistry . S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart 2004, ISBN 3-7776-1221-9 , p. 630 ff .
- ^ Zerong Wang: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents . John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey 2009, ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8 , pp. 2942-2945 .