Imiquimod
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
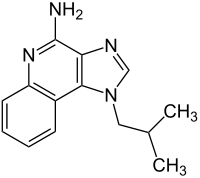
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Imiquimod | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 14 H 16 N 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 240.30 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
292-294 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Imiquimod is a drug from the group of antivirals that is used to treat small, superficial basal cell skin cancer ( basalioma ), actinic keratosis and genital warts ( condylomata acuminata ), as well as cutaneous warts. Imiquimod was developed by 3M . It is sold worldwide, in Europe by the Swedish pharmaceutical company MEDA under the trade name Aldara ® .
Resiquimod (R848), which is still in development and has the same mechanism of action, but is much more effective and binds to two toll-like receptors (TLR), is regarded as the successor to imiquimod .
Mode of action
Imiquimod is an immunomodulator . It does not destroy the viruses and cancer cells, but rather it activates the skin's immune system so that it can fight the viruses or the tumor itself. Imiquimod provokes an inflammatory reaction by binding to TLR7 . This is a surface molecule of cells of the immune system, in particular of macrophages , which, if suitable substances attach to them, conveys the signal “foreign” (“not belonging to the body”) to the immune system.
In contrast to conventional methods in which warts cut, frozen or cauterized be Imiquimod does not damage the skin.
Contraindications
Imiquimod should not be applied to open wound areas or irritated skin. In addition, it should only be used during pregnancy after an intensive risk-benefit assessment . It cannot be taken during breastfeeding , as the active ingredient passes into breast milk.
The active ingredient should not be used in children and adolescents under 18 years of age, as insufficient research results are available for this group of patients.
Side effects
Imiquimod often causes skin irritation ( erythema , erosion, excoriation / flaking and edema). Phimoses have occurred when used in the foreskin area . There are isolated cases of severe systemic side effects - including the capillary leak (Engl. Capillary leak syndrome ) - described.
In addition, the following side effects are common when taking imiquimod:
- Nausea ,
- Joint pain ,
- Urination disorders,
- Infection ,
- Tiredness ,
- Muscle aches,
- Irritation or burning sensation (on site)
In psoriatic patients , topically applied imiquimod can trigger a systemic flare-up of psoriasis .
Admission status
In March 2011, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved imiquimod for the United States (Zyclara ® ) for the treatment of external and perianal genital warts. Approval for actinic keratoses followed in July 2011.
Hints
When used in the genital area, imiquimod can impair the tear resistance of condoms.
Trade names
Imiquimod is commercially available in Germany, Austria and Switzerland under the name Aldara and in the USA under Zyclara.
literature
- Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery . 2005, 9 (5), pp. 209-214, doi : 10.1007 / s10227-005-0148-6 (systematic review and meta-analysis in actinic keratosis).
- Journal of Investigative Dermatology . 2006, 126 (6), pp. 1251-1255, doi : 10.1038 / sj.jid.5700264 (systematic review and meta-analysis in actinic keratosis).
- Dermatology . 2006, 213 (3), pp. 218–223, doi : 10.1159 / 000095039 (systematic review and meta-analysis for genital warts).
- International Journal of Dermatology . 2006, 45, pp. 1464-1465, doi : 10.1111 / j.1365-4632.2006.02980.x (induction of psoriasis by imiquimod).
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on imiquimod. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 1, 2014.
- ↑ a b Imiquimod data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 5, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Specialist information Aldara ® (PDF; 108 kB) as of April 2010, accessed on April 10, 2012.
- ^ A b Peter Fritsch: Dermatology and Venereology. 2nd Edition. Springer Verlag, 2004, ISBN 3-540-00332-0 .
- ↑ What are the contraindications (contraindications)? Retrieved August 25, 2017 .
- ^ PA Fanti, E. Dika, S. Vaccari, C. Miscial, C. Varotti: Generalized psoriasis induced by topical treatment of actinic keratosis with imiquimod . In: International Journal of Dermatology . 45 (2006), pp. 1364-1365, doi : 10.1111 / j.1365-4632.2006.02980.x .
- ^ Report (PDF; 59 kB) from the FDA to Graceway Pharmaceuticals with reference to approval, March 24, 2011.
- ↑ FDA Approves Zyclara ® (imiquimod) Cream, 2.5% for the Treatment of Actinic Keratoses ( Memento from September 19, 2012 in the web archive archive.today ) , distributor's press release from July 18, 2011 (Reuters).