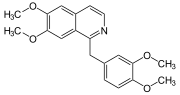
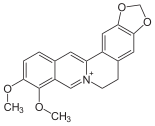
Isoquinoline alkaloids

The isoquinoline alkaloids are natural substances from the group of alkaloids , which are chemically derived from isoquinoline . These represent the largest group among the alkaloids.
Due to the different basic chemical structures, the isoquinoline alkaloids can be further subdivided. The most common structural types are the benzylisoquinolines and the aporphines . According to current knowledge, a total of around 2500 chemical compounds are counted among the isoquinoline alkaloids, which are mainly formed by plants.
Well-known representatives
Occurrence in nature
The isoquinoline alkaloids are primarily formed in the plant families of the Papaveraceae , Berberidaceae , Menispermaceae , Fumariaceae and Ranunculaceae .
The opium poppy , which belongs to the Papavaraceae family, plays a major role in this , as the isoquinoline alkaloids morphine , codeine , papaverine , noscapine and thebaine can be detected in the milky sap it contains , which is also known as opium . In addition to the opium poppy, there are other poppy plants, such as celandine , in which isoquinoline alkaloids occur. This milky juice contains berberine, which is also found in other plant families, such as the Berberidaceae. A representative of the Berberidaceaen with the ingredient berberine is the common barberry .
Tubocurarine belongs to the subgroup of bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids ; it occurs in the hairy cartilage tree. There the tubocurarine is extracted from the bark and roots .
Opium poppy , contains morphine, codeine and papaverine
Celandine , contains berberine
Common barberry , contains berberine
effect
Generally speaking, isoquinoline alkaloids can have different effects. The opium alkaloids can have sedative , psychotropic or analgesic properties.
Morphine and codeine are used as analgesics.
Papaverine, on the other hand, has an antispasmodic effect if it comes from the smooth muscles , such as occurs in humans in the gastrointestinal tract or in blood vessels . That is why it is used as a spasmolytic .
Tubocurarine impairs the transmission of stimuli in nervous systems , so that symptoms of paralysis can occur in the affected organism .
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Gerhard Habermahl, Peter E. Hammann, Hans C. Krebs, Waldemar Ternes: natural products. Springer-Verlag, Berlin / Heidelberg 2008, ISBN 978-3-540-73733-9 , doi: 10.1007 / 978-3-540-73733-9 , pp. 176-187.
- ↑ Bettina Ruff: Chemical and biochemical methods for the stereoselective synthesis of complex natural substances. Verlag Logos, Berlin 2012, ISBN 978-3-8325-3121-8 , p. 8. ( limited preview in Google book search)
- ↑ a b Jennifer M. Finefield, David H. Sherman, Martin Kreitman, Robert M. Williams: Enantiomeric Natural Products: Occurrence and Biogenesis. In: Angewandte Chemie. , 2012, 124 (20), pp. 4886-4920, doi: 10.1002 / anie.201107204 , pp. 4905-4915.
- ↑ A. Husemann, T. Husemann: The plant substances in chemical, physiological, pharmacological and toxicological terms. Berlin 1871, pp. 245-253. (Digitized version of the Bavarian State Library) .
- ↑ Entry on berberine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 13, 2017.
- ↑ Rudolf Hänsel, Josef Hölzl: Textbook of pharmaceutical biology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin / Heidelberg / New York 2012, 1996, ISBN 3-642-64628-X , doi: 10.1007 / 978-3-642-60958-9 , p. 302.
- ↑ Rainer Nowack: Emergency manual poisonous plants: A determination book for doctors and pharmacists. Springer-Verlag, Berlin / Heidelberg 1998, doi: 10.1007 / 978-3-642-58885-3 , p. 258.
- ↑ Jens Frackenpohl: Morphine and opioid analgesics. In: Chemistry in Our Time . 2000, 34, No. 2, doi : 10.1002 / 1521-3781 (200004) 34: 2 <99 :: AID-CIUZ99> 3.0.CO; 2-X , pp. 99-112.
- ↑ Franz v. Bruchhausen, Gerd Dannhardt, Siegfried Ebel, August-Wilhelm Frahm, Eberhard Hackenthal, Ulrike Holzgrabe: Hager's Handbook of Pharmaceutical Practice. 5th edition. Springer-Verlag, Berlin / Heidelberg 1994, doi: 10.1007 / 978-3-642-57880-9 , p. 16.
- ↑ Heinz Lüllmann, Klaus Mohr, Lutz Hein: Pharmacology and Toxicology. 16th edition. Georg-Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart / New York 2006, ISBN 3-13-368516-3 , pp. 255-258.