Potassium citrate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
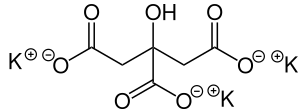
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Potassium citrate | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 5 K 3 O 7 • H 2 O | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless and odorless crystals |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.98 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
> 180 ° C (release of crystal water) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
> 230 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Potassium citrate is the potassium salt of citric acid . It is a white, slightly hygroscopic , odorless powder with a slightly salty taste. It is used in medicine, food technology as well as in the pharmaceutical and cosmetics industries.
presentation
Potassium citrate is industrially synthesized from citric acid, which may be obtained using genetically modified organisms .
use
medicine
Potassium citrate is primarily used to treat kidney stones . It is absorbed very quickly by the body after ingestion ; an excess of potassium or citrate ions is excreted in the urine . Potassium citrate is an effective prevention against kidney stones from uric acid (a side effect of gout ), cystine or calcium oxalate , whereby the active principle with the organic stones the alkalization of the urine and with oxalate the increase of the solubility through complexation . The effectiveness does not apply to all stone compositions. A study of 500 patients with recurrent kidney stones showed that treatment with potassium citrate reduced the average number of stones per year from two to half a year.
Like many other potassium salts, potassium citrate can prevent cardiac arrhythmias caused by a lack of potassium in the blood. In addition, clinical studies have shown that potassium citrate counteracts calcium loss via the kidneys and calcium breakdown from the bones. A prospective controlled intervention study in 161 postmenopausal women with osteopenia showed that the partial neutralization of diet-induced acid exposure (using 30 mmol potassium from potassium citrate per day, corresponds to 3.24 g potassium citrate) over a period of twelve months significantly increased bone density and bone structure significantly improved. Potassium citrate was just as effective as raloxifene , an estrogen receptor modulator used in the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. In addition, potassium citrate has an antihypertensive effect and has been shown to reduce blood pressure as effectively as potassium chloride .
Food technology
Potassium citrate is used as an acidifier and acid regulator , as well as a complexing agent or melting salt . It is often found as an acidulant in beverages such as lemonades or is used for gelling with pectin . It is generally approved in the EU as a food additive with the number E 332 without maximum quantity restriction ( quantum satis ) for all foods.
Trade names
- Potassium Verla (D)
- Urocit (CH)
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on E 332: Potassium citrates in the European database on food additives, accessed on June 27, 2020.
- ↑ Entry on POTASSIUM CITRATE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on July 1, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i data sheet Tripotassium citrate monohydrate, 99 +% from AlfaAesar, accessed on December 26, 2019 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ External identifiers of or database links to potassium citrate monohydrate : CAS number: 6100-05-6, EC number: 612-062-1, ECHA InfoCard: 100.127.864 , PubChem : 2735208 , ChemSpider : 2016906 , Wikidata : Q27133400 .
- ↑ transGEN: citric acid E 330
- ↑ Sakhaee K, Nicar M, Hill K, Pak CY: Contrasting effects of potassium citrate and sodium citrate therapies on urinary chemistries and crystallization of stone-forming salts . In: Kidney Int . 24, No. 3, September 1983, pp. 348-352. PMID 6645208 .
- ↑ Ettinger B, Pak CY, Citron JT, Thomas C, Adams-Huet B, Vangessel A: Potassium-magnesium citrate is an effective prophylaxis against recurrent calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis . In: J. Urol . 158, No. 6, December 1997, pp. 2069-2073. PMID 9366314 .
- ↑ Robinson MR, Leitao VA, Haleblian GE, et al. : Impact of long-term potassium citrate therapy on urinary profiles and recurrent stone formation . In: J. Urol . 181, No. 3, March 2009, pp. 1145-1150. doi : 10.1016 / j.juro.2008.11.014 . PMID 19152932 .
- ↑ a b Jehle S et al .: Partial neutralization of the acidogenic western diet with potassium citrate increases bone mass in postmenopausal women with osteopenia. In: J Am Soc Nephrol . (2006) 17: 3213-3222, PMID 17035614 .
- ↑ Marangella M et al .: Effects of potassium citrate supplementation on bone metabolism. Calcif Tissue Int (2004) 74: 330-335, PMID 15255069 .
- ↑ Sellmeyer DE et al .: Potassium citrate prevents increased urine calcium excretion and bone resorption induced by a high sodium chloride diet. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2002) 87: 2008-2012, PMID 11994333 .
- ↑ He et al .: Effect of short-term supplementation of potassium chloride and potassium citrate on blood pressure in hypertensives . In: Hypertension. (2005) Apr; 45 (4): 571-4, PMID 15723964 .