Kleinspot genet
| Kleinspot genet | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Small-spotted genet in the roof structure of the dining room of a safari camp in Tanzania |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Genetta genetta | ||||||||||||
| ( Linnaeus , 1758) |
The Kleinfleck gorse cat ( Genetta genetta ), also known as the European gorse cat , is a type of gorse cat that was first described by Linnaeus in 1758 as Viverra genetta .
Appearance
The gorse cat is with a head-torso length of about 50 centimeters and a tail length of about 45 centimeters about as big as a house cat , but more elongated. The fur has a gray-brown basic color, on which black spots are arranged in longitudinal rows. The tail has eight to ten black rings. The tip of the tail is mostly white. The muzzle is pointed, the legs short and the ears large. The claws are short and retractable. The auricles are well developed and mobile. Small-spotted genet cats have 40 teeth. The animal has a strong smell of musk . The anal gland only secretes a small amount of fat, musky-smelling moisture; if threatened, a foul-smelling secretion is given off.
Distribution and subspecies
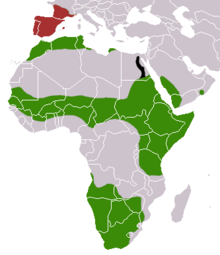
The Kleinfleck genet occurs in five subspecies in Africa , Europe and on the Arabian Peninsula .
- Genetta genetta genetta , North Africa from Morocco to Libya and south-western Europe
- Genetta genetta dongolana , East and Northeast Africa
- Genetta genetta grantii , southwest of the Arabian Peninsula, Yemen and Oman
- Genetta genetta genetta , Angola, Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe and South Africa
- Genetta genetta senegalensis , West Africa
In Africa, three separate areas of distribution are settled: the northern edge of the Sahara ( Morocco , Algeria , Tunisia and Libya ), savannah areas in a broad strip of sub-Saharan Africa from West to East Africa and in southern Africa. On the Arabian Peninsula, the distribution is limited to the coastal regions of Saudi Arabia , Yemen and Oman .
The stocks in Europe are considered to have been introduced by humans. The species can be found in southern France and on the Iberian Peninsula ( Spain and Portugal ), as well as on the Balearic islands of Mallorca , Ibiza and Cabrera . There are regular sightings in Germany and Belgium .
Habitats
The range of populated habitats is very wide. Trees and bushes or rocks are often present, and various types of forests and bushland are inhabited. The species is often found in the vicinity of human settlements, but seems to avoid dense rainforest and extremely arid regions. In Europe, oak forests and olive groves are typical habitats. The altitude ranges up to 2,600 m in the High Atlas (Morocco) and at least 3,000 m in the highlands of Ethiopia . In central Spain a maximum of 1,400 m is reached.
behavior
Small-spotted genet cats are excellent jumpers and climbers who can move around without injury even on thorny branches. The nocturnal and shy animals usually live alone, very rarely only in families. During the day the gorse cats sleep in hiding, at night they go hunting. The gestation period for genet cats is ten to twelve weeks, and two to four young are born per litter. You are still naked and blind. After a year they leave their mother. Genet cats make noises similar to cats: growling when excited, hissing as a threat, purring when they are comfortable, and meowing.
Small -spotted genet cats mainly prey on small mammals , as well as birds , reptiles , amphibians, fish and insects . Occasionally they also eat berries, other fruits or rob nests. In one located in the southwest of France forest with rocky regions, the animals fed 78% of small mammals, including the wood mouse , the bank vole , the West vole , field mice , Sorex , moles , the shrew , the water shrew and occasionally the weasel and the ermine . Birds and insects, especially beetles and grasshoppers , made up about 10% of the diet, and amphibians, reptiles, rabbits and fish made up one percent or less. Grasses, berries and other fruits were ingested on plants (10 to 13%).
Danger
Due to the large distribution area and the frequency of the species, it is not considered endangered by the IUCN .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Jacobus du P. Bothma: Carnivore Ecology in Arid Lands. Springer, 1998, ISBN 3-662-03587-1 , chap. 6.2.2.
- ^ A b c J. Jennings AP & G. Veron: Family Viverridae. In: DE Wilson. & RA Mittermeier (Eds.): Handbook of the Mammals of the World. Volume 1: Carnivores , Lynx Edicions, Barcelona, 2009, ISBN 978-84-96553-49-1 . Page 217 a. 218.
- ↑ a b genetta genetta in the endangered Red List species the IUCN 2012. Posted by: Herrero, J. & Cavallini, P., 2008. Accessed on November 3 2,012th
literature
- Chris and Tilde Stuart: Southern, Central and East African Mammals. Struik Publishers, 1992, ISBN 0-88359-028-X .
- S. Aulagnier, P. Haffner, AJ Mitchell-Jones et al. a .: Guide des mammaifères d'Europe, d'Afrique du Nord et du Moyen-Orient. at Delachaux & Niestlé, Paris 2010, ISBN 978-2-603-01702-9 .
Web links
- Genetta genetta in the endangered Red List species the IUCN 2006. Posted by: Mustelid Specialist Group, 1996. Retrieved on 12 May, 2006.