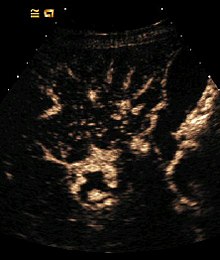
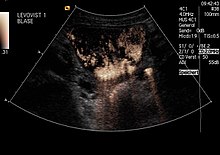
Contrast enhanced ultrasound
At contrast-enhanced ultrasound - also CEUS (contrast enhanced ultrasound) - ultrasound contrast agents in ultrasound or echocardiography used. These contrast agents are gas-filled microbubbles ( micro bubbles ), which in most applications intravenously given and are either respirable or non-respirable. Contrast media are very echogenic .
Applications
abdomen
- Detection and characterization of liver tumors : The pattern and the time of contrast agent uptake of changes in the liver make it possible in many cases to assign an exact species. Here one makes use of a special feature of the liver. In contrast to most other organs (with the exception of the pituitary gland ), the liver has a dual blood supply: in addition to the hepatic artery , the organ is supplied via the portal vein , which supplies nutrient-rich blood from the intestine. Sprayed contrast agent into a vein in the arm, so this is first the arteries to the liver enter (by, amongst others, the biliary tract with oxygen to supply), then the contrast agent is flowing down into the hepatic veins . The influx of the contrast agent in the portal vein takes on longest (30–40 s), as the blood first circulates in the intestine and then reaches the liver. The liver's own tissue will therefore also contain contrast media in this so-called late phase. Metastases of non-liver tumors naturally do not contain a portal vein system and therefore appear contrast-free (dark).
Some tumors are so typical in contrast-enhanced ultrasound that a liver biopsy is now dispensed with.- Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH): Is supplied by a vascular system with a wheel spoke pattern.
- Hemangioma : A hemangioma is deduced from the time course of the contrast medium flooding from outside to inside (" iris diaphragm phenomenon").
- Kidney perfusion : This is where areas not supplied with blood (e.g. kidney infarction) can be mapped at an early stage.
- Representation of pancreatic tumors: Here contrast sonography can be helpful in differentiating masses. In particular, the highly vascularized neuroendocrine tumors can be distinguished from the adenocarcinomas, which are prognostically much less favorable and hardly absorb contrast enhancers.
- Injuries to internal organs: A hematoma (accumulation of blood) in the organ can be observed here. In addition, the contrast agent shows even the slightest bleeding into the free abdominal cavity.
cardiology
For the detection of cardiac shunts such as the persistent foramen oval , the examination with non-respirable contrast media is considered to be the gold standard in a transesophageal echocardiography . Respiratory contrast media are recommended by the European Association of Echocardiography in its expert consensus for suboptimal stress echocardiography examinations in order to improve endocardial delimitation and thus to be able to assess wall movement more reliably. Some ultrasound systems can simultaneously display the myocardial perfusion , which is reduced in coronary heart disease under stress, but also in acute myocardial infarction .
gynecology
In the area of diagnostics when the desire to have children is unfulfilled, hystero-contrast salpingography is used to check the patency of the fallopian tubes .
Vascular surgery
For follow-up after EVAR (endovascular aortic repair) of an abdominal aortic aneurysm. An endoleak can be diagnosed or excluded using contrast-enhanced ultrasound.
Pediatrics
see main article micturition urosonography
To rule out reflux of urine from the bladder into the kidney : This examination, called micturition urosonography (MUS), can replace the previous X-ray examination with contrast agent (micturition cystourogram, MCU). In this way, a reflux test is possible without exposure to radiation . Since the sensitive gonads are regularly included in the useful beam during the X-ray examination, this is a great advantage.
In order to show the urethra in boys (since boys can have urethral valves , but girls not), the first examination in boys is usually carried out as a classic MCU, but follow-up examinations are then carried out as MUS.
Microbubbles
Respiratory and non-respiratory contrast media are available on the market which consist of microbubbles and differ essentially in their envelope and gas content. They are around 1 to 4 μm in size.
In the ultrasound field microbubbles begin to oscillate . At higher sound pressures , non-linear vibrations of high amplitude also arise , which can be easily separated from signals from the tissue and thus make it possible to observe the blood supply to the tissue.
- Microbubbles with increasing sound pressure amplitudes of the ultrasound
Individual evidence
- ^ OII Soliman et al .: The use of contrast echocardiography for the detection of cardiac shunts. In: Eur J Echocardiography. 8, 2007, pp. S2-S12. doi: 10.1016 / j.euje.2007.03.006
- ↑ R. Sicari include: Stress echocardiography expert consensus statement. In: European Journal of Echocardiography. 9, 2008, pp. 415-437. doi: 10.1093 / eurheartj / ehn492
literature
- T. Albrecht et al .: Guidelines for the use of contrast agents in ultrasound. In: Ultrasound Med. 25 (4), Aug 2004, pp. 249-256.
- H. Becher: Contrast echocardiography: clinical applications and future prospects. In: heart. 27 (3), May 2002, pp. 201-216.
- M. Riccabona: Contrast ultrasound of the urethra in children. In: Eur Radiol. 13 (7), Jul 2003, pp. 1494-1495.
- S. Tinkov, R. Bekeredjian, G. Winter, C. Coester: Microbubbles as ultrasound triggered drug carriers. In: J Pharm Sci . 98, 2009, pp. 1935-1961. PMID 18979536 (Review).