Leucopter
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Leucopter | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 5 N 5 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
fine colorless crystals |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 195.14 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
sparingly soluble in water: approx. 1.25 g l −1 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Leucopterin is a chemical compound from the group of pteridines .
Occurrence
Leucopterin occurs in the white wings of a species of butterfly.

In 1926, Clemens Schöpf and Heinrich Otto Wieland isolated the natural substance leucopterin from the wings of white lobsters of the species Pieris brassicae and Pieris napi . This wing pigment was called "leucopterin" (from the Greek leukos , 'white' and pteron , 'wing'). The white color of the butterfly's wings does not come from the dye, but from the “reflection of light on the scales in which air is trapped”.
synthesis
To demonstrate the structure, Robert Purrmann synthesized the compound in 1940 by mixing 2,4,5-triamino-1,6-dihydropyrimidin-6-one (2,4,5-triamino-6-hydroxypyrimidine) with an excess of oxalic acid with heating merged.
properties
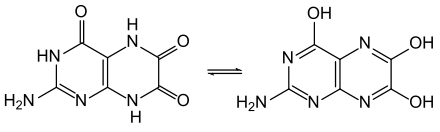
Like pterine , leucopterine also has the possibility of keto-enol tautomerism , better here lactam-lactim tautomerism : 2-amino-5,8-dihydro-4,6,7 (1H) -pteridintrione versus 2-amino-4,6 , 7-pteridine triol. Further tautomers are conceivable. A comparison of the UV spectrum in solution with that of other substituted pteridines indicates that the lactam structure shown in the info box is present.
Leucopterin is a weak acid and therefore dissolves in alkalis, e.g. B. Soda solution or dilute sodium hydroxide solution . When 2N hydrochloric acid is added, the colorless solid precipitates again, which Schöpf and Purrmann used to purify the substance. The acidity is highest for the N (8) -H group, followed by N (3) -H and at the end N (5) -H. Sodium, barium and ammonium salts were made from the compound. Leucopterin forms almost colorless crystals that contain 0.5 molar equivalents of crystal water (hemihydrate).
biosynthesis
A radiochemical study on caterpillars and pupae of the cabbage white butterfly ( Pieris brassicae L.) with 14 C-labeled substances came to the conclusion that leucopterin in the butterfly arises from the purine derivative guanine or guanosine , with xanthopterine probably being the immediate precursor. The oxo group at C-8 can be introduced by the enzyme xanthine oxidase .
literature
- Robert Purrmann, Pterine, Advances in Chemistry of Organic Natural Products 4 , 64–86 (1945). This early overview describes the historical development of the knowledge about leucopterin and other pterin derivatives.
Individual evidence
- ^ Entry on Leucopterin. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 9, 2014.
- ↑ Beilstein's Handbook of Organic Chemistry, 4th supplementary work, Vol. 26 , p. 4017.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ A b Albert Gossauer: Structure and reactivity of biomolecules , Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta, Zurich, 2006, p. 504, ISBN 978-3-906390-29-1 .
- ^ Clemens Schöpf, Heinrich Wieland: About the leucopterin, the white pigment of the wings of the cabbage white butterfly (Pieris brassicae and P. napi). In: Reports of the German Chemical Society , 59 , 2067-2072 (1926), doi : 10.1002 / cber.19260590865 .
- ↑ Clemens Schöpf, Rolf Reichert: To the knowledge of the Leukopterins , Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie , 548 , 82–94 (1941), doi : 10.1002 / jlac.19415480108 .
- ↑ Robert Purrmann: About the wing pigments of butterflies. VII. Synthesis of Leucopterin and Nature of Guanopterin . Justus Liebig's Annalen der Chemie , 544 , 182-190 (1940), doi : 10.1002 / jlac . 19405440111 .
- ^ Robert Purrmann: Constitution and synthesis of the so-called anhydroleukopterin. About the wing pigments of the butterflies XII . Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie , 548 , 284-292 (1941); doi : 10.1002 / jlac.19415480121 . PDF
- ↑ Wolfgang Pfleiderer, Manfred Ruckwied, On the structure of leukopterin, Chem. Ber. 94: 118-124 (1961).
- ↑ Friedrich Weygand, H. Simon, G. Dahms, M. Waldschmidt, HJ Schliep, H. Wacker, On the biogenesis of leucopterin. Angewandte Chemie , 73 , 402-407 (1961). doi : 10.1002 / anie.19610731111