Limonia acidissima
| Limonia acidissima | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Indian crab apple |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the genus | ||||||||||||
| Limonia | ||||||||||||
| L. | ||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the species | ||||||||||||
| Limonia acidissima | ||||||||||||
| L. |
Limonia acidissima , also called Indian crab apple or elephant apple , is the only species of the monotypic plant genus Limonia within the family of the diamond plants (Rutaceae). It iswidespreadin the arid plains on the Indian subcontinent: Bangladesh , India , Pakistan , Sri Lanka and in the western Himalayas and from Southeast Asia to Java . The fruits are used as fruit .
description
Appearance and leaf
Limonia acidissima grows as a deciduous, small tree that reaches heights of about 9 meters. The bark is thick and hard.
The alternate and spirally arranged leaves on the branches are divided into short petioles and leaf blades. The petiole and leaf rhachis are narrowly winged. The 7.5 to 12.5 cm long, dark green, leathery leaf blade is pinnate unpaired and the five or seven leaflets are arranged opposite one another on the leaf hachis. The leaflets are 25 to 35 mm long and 10 to 20 mm wide and obovate with a smooth or slightly notched edge and a rounded end that has a notch. The leaves are dotted with glands and smell slightly of lemons when they are ground. The leaf axils are about 15 mm long with thorns .
Inflorescence and flower
The flowering period in Pakistan extends from March to May. There is polygamy . however, the flowers are mostly hermaphroditic. The flowers are in terminal or lateral, loose, panicle inflorescences .
The fragrant flowers are radial symmetry and usually five, rarely four or six-fold with a double flower envelope and a diameter of about 1.25 cm. The sepals are egg-shaped. The matt red petals are spread out, elongated to narrow obovate or elliptical. There are two circles with five or six stamens . The subtle stamens are hairy at their base. The seated scar is spindle-shaped.
Fruit and seeds
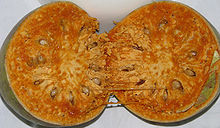
The berries (armored berries ) are round to oval with a diameter of 5 to 12.5 cm with a hard, woody, grayish-white, about 6 mm thick, scabbed skin. The fragrant, astringent, sour or sweet fruit pulp is brown and floury. There are many, small, brown seeds that are woolly hairy throughout the pulp.
Chromosome number
The number of chromosomes is 2n = 18.
use
The fruit bowl is opened with a hammer. The fruit pulp is eaten raw with or without sugar. You can also make a soft drink or ice cream with coconut milk or palm syrup. It is also used in chutneys or jams.
The fruit peel is also made into small containers.
The unripe fruits are used in folk medicine in India. The astringent effect is used, for example, against diarrhea and dysentery . Leaves, bark, roots and fruit pulp are used against snakebites.
The triturated bark is used in Myanmar for thanaka , a cosmetic.
Systematics
The genus Limonia was established in 1762 by Carl von Linné in Species Plantarum , 2nd edition, p. 554. The type and only species in the genus is Limonia acidissima . Limonia Gaertn is a homonym . published in Joseph Gaertner : De Fructibus et Seminibus Plantarum ... , Volume 1, 1788, p. 278. A synonym for Limonia L. is Feronia Corrêa . Synonyms for Limonia acidissima L. are: Feronia elephantum Corrêa , Feronia limonia (L.) Swingle , Schinus limonia L.
The genus Limonia belongs to subtribe Citrinae from the tribe Aurantieae in the subfamily Aurantioideae within the family of Rutaceae .
Common names
Trivial names in other languages are:
- English : Wood Apple, Elephant Apple, Monkey Fruit, Curd Fruit
- Oriya : Kaintha
- Telugu : Vellaga Pandu
- Tamil : Vilam Palam (விளாம் பழம்)
- Bengali : Koth Bel (কৎ বেল)
- Hindi : Kaitha (कैथा), Kath Bel
- Sinhala : Divul
- Marathi : KavaTH (कवठ).
- Sanskrit : Kapittha (कपित्थ), Dadhistha, Surabhicchada, Kapipriya, Dadhi, Puṣpapahala, Dantasātha, Phalasugandhika, Cirapākī, Karabhithū, Kanṭī, Gandhapatra, Grāhiphala, Kaṣāyāmlaphala
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k genus Limonia and species Limonia acidissima in the Flora of Pakistan .
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k Feronia elephantum on TrekNature .
- ^ Limonia acidissima at Tropicos.org. In: IPCN Chromosome Reports . Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis
- ↑ Helmut Köllner, Axel Bruns: Myanmar (Burma) , 1998, Hunter Publishing, ISBN 3-88618-415-3 , p. 18
- ↑ First publication scanned at biodiversitylibrary.org .
- ↑ Entry in Tropicos .
- ^ A b Limonia in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland.
- ^ SG Joshi, Medicinal Plants, Oxford & IBH Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi, 2004, ISBN 81-204-1414-4 , p.347
Web links
- The Wood Apple (English)
- Pandanus Database . (English)
- Walter T. Swingle: The Botany of Citrus and Its Wild Relatives . In: Walter Reuther, Herbert John Webber, Leon Dexter Batchelor (eds.): The Citrus Industry . tape 1 . University of California - Division of Agricultural Sciences, 1967, Chapter 3 ( online ). (English)