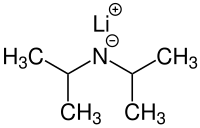
Lithium diisopropylamide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Lithium diisopropylamide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 14 LiN | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
self-igniting, moisture-sensitive solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 107.12 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
solid (but mostly in solution) |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.86 g cm −3 (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in hexane |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) is the lithium salt of diisopropylamine . It is a strong base used in the organic chemistry often for deprotonation of CH-acid is used compounds. Because of the steric hindrance caused by the space-filling isopropyl radicals, LDA is not very nucleophilic . The pK S value of the conjugate acid is 40. It is thus possible, weakly acidic CH compounds, such as carbonyl compounds in α-position to deprotonate and this characterized in enolates to transfer. LDA is usually commercially available as a solution in diethyl ether or THF . In these solutions it forms dimeric structures. In non-polar solvents such as. B. toluene , however, it is a mixture of trimers, tetramers, pentamers and higher oligomers.
Manufacturing
LDA can be made from diisopropylamine with organo-lithium compounds such as phenyllithium or butyllithium . A cheaper way is to react elemental lithium with diisopropylamine in the presence of styrene .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on lithium diisopropylamide. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on August 16, 2015.
- ↑ a b c d data sheet lithium diisopropylamide from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on August 16, 2015 ( PDF ).
- ↑ KPC Vollhardt, NE Schore: Organic Chemistry. 3. Edition. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2000, ISBN 3-527-29819-3 .
- ↑ PG Williard, JM Salvino: Synthesis, Isolation, and Structure of an LDA-THF Complex. In: J. Org. Chem. 58 (1), 1993, pp. 1-3, doi: 10.1021 / jo00053a001 .
- ^ R. Neufeld, M. John, D. Stalke: Elucidation of the donor base-free aggregation of lithium diisopropylamide in hydrocarbons using a DOSY method. In: Angew. Chem. 127 (1), 2015, pp. 7100-7104, doi: 10.1002 / anie.201502576 .
- ↑ R. Neufeld: DOSY External Calibration Curve Molecular Weight Determination as a Valuable Methodology in Characterizing Reactive Intermediates in Solution. Dissertation. Georg August University, Göttingen 2016.
- ↑ AP Smith, JJS Lamba, CL Fraser: Efficient Synthesis of Halomethyl-2,2'-Bipyridines: 4,4'-Bis (chloromethyl) -2,2'-Bipyridine In: Organic Syntheses . 78, 2002, p. 82, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.078.0082 ; Coll. Vol. 10, 2004, p. 107 ( PDF ).
- ↑ MT Reetz, WF Maier: Simple representation of lithium diisopropylamide on a molar scale. In: Liebig's annals . 10, 1980, pp. 1471-1473, doi: 10.1002 / jlac.198019801002 .