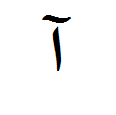Madda
Madda ( Arabic مدة, from مد madd "elongation", "elongation") is a character in the Arabic script . It can (in non- Qur'anic Arabic) only stand on the alif and looks like a tilde (~).
The Alif with Madda replaces the sequence of letters أاand stands for the sound sequence / ʾā / ( Hamza + long a). That is, Madda is used when a Hamza, which has Alif as a carrier letter, is followed by a long a-sound (ā) written with Alif. This avoids the clash between two Alif. So z. B. the word ʾāl ("clan") notأال rather آل written.
In Persian and other languages based on the Arabic alphabet, an added alif can also stand for a single long a, usually at the beginning of a word. In editions of the Qur'an it is a pure sign of elongation: It can also appear above Vav and Ya and “does not contain” a Hamza.
Madda in Unicode
Madda is coded in combination with the carrier-Alif and as a combining symbol .
| Unicode codepoint | U + 0622 | U + 0653 |
|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | ARABIC LETTER ALEF WITH MADDA ABOVE | ARABIC MADDAH ABOVE |
| HTML | & # 1570; | & # 1619; |
| ISO 8859-6 | 0xc2 |