McMurdo Sound
| McMurdo Sound | ||
|---|---|---|
|
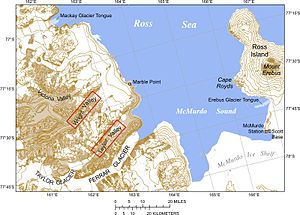
Location of McMurdo Sound, English map labeling |
||
| Waters | Ross Sea | |
| Land mass | Victoria Land and Ross Island , Antarctica | |
| Geographical location | 77 ° 40 ′ S , 165 ° 0 ′ E | |
|
|
||
| width | 56 km | |
| depth | 56 km | |
|
Ocean floor with various invertebrate soil organisms in low bay Explorers Cove |
||
The McMurdo Sound ( English McMurdo Sound ) is a 56 km long and equally wide bay of the Ross Sea , which extends along the Scott coast of the East Antarctic Victoria Land. Its western border runs between the northern reaches of the Brown Peninsula in the south and Cape Roberts in the north. Its northern extent is limited by a line between Cape Roberts and Cape Bird at the northwest end of Ross Island . The eastern boundary corresponds to the coastline of Ross Island between Cape Bird and New Zealand's Scott Base on the Hut Point Peninsula . The southern border line runs from Scott Base past the northern foothills of White Island back to the starting point on the Brown Peninsula.
Research history
McMurdo Sound was discovered on February 17, 1841 by the British navigator and explorer James Clark Ross . Just one year later, the bay was named after the British Lieutenant Archibald McMurdo (1812-1875), who served as an officer on board the HMS Terror during Ross' Antarctic expedition .
McMurdo Sound was not forgotten in the following years. Since it is one of the few coastal stretches of Antarctica that is seasonally ice-free, some of the most famous polar expeditions began on the sound. The Discovery Expedition (1901–1904) and the Terra Nova Expedition (1910–1913), both led by Robert Falcon Scott , were based here, as was the Nimrod Expedition (1907–1909) led by Ernest Shackleton .
The United States established McMurdo Station on Ross Island in 1955 . With a staff of more than 200 researchers, it is the largest in Antarctica. In the immediate vicinity is the Scott Base built by New Zealand at Pram Point .
In 2011, researchers discovered an active leak at a depth of ten meters, which they were able to research scientifically from 2016. The results of this research were published in 2020 in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society . According to them, the leak has been releasing methane for years .
Icebergs
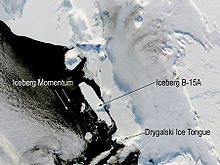
McMurdo Sound is one of the few stretches of coastline in Antarctica that is free of ice at certain times of the year. In recent years, the international mass media reported about the sound because icebergs up to 200 km long blocked the sea section. In December 2000, the 11,600 km² iceberg B-15 broke off the Ross Ice Shelf . from. To date, this is the largest iceberg ever measured. Since such icebergs have formed more and more frequently in recent years, researchers see them as an indication of global warming .
Because of the many icebergs and the limited absence of ice as well as many penguin colonies , the sound is not only interesting for research, but also for nature filmmakers and photographers . A small tourist business has also developed.
literature
- GEO edition 11/2006, topic Antarctica: "McMurdo-Sound - An expedition at the end of the world", London 1999
Web links
- McMurdo Sound on geographic.org (English)
- Images of the iceberg B-15
Individual evidence
- ^ John Stewart: Antarctica - An Encyclopedia . Vol. 2, McFarland & Co., Jefferson and London 2011, ISBN 978-0-7864-3590-6 , p. 981 (English).
- ↑ James Clarke Ross: Voyage of Discovery and Research in the Southern and Antarctic Regions, during the Years 1838–1843 , Vol. I, John Murray, London 1847, pp. 244–245
- ↑ "Nothing good". Methane leakage in the sea floor raises questions. In: ORF . July 22, 2020, accessed July 27, 2020 .