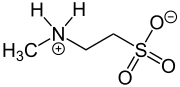
N -methyl taurine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | N -methyl taurine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
2-methylamino-ethanesulfonic acid |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 9 NO 3 S | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 139.17 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
246-249 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
N -methyltaurine or 2-methylaminoethanesulphonic acid is an aminosulphonic acid that, like an amino acid, is in a crystalline state and in polar solvents as a zwitterion . In contrast to the widespread taurine , N -methyltaurine has so far only been found in nature in red algae , where it is formed by methylation of taurine. Because of its high polarity and the relatively good solubility of its alkaline earth metal salts, it is suitable for esterification (actually amide formation ) with long-chain carboxylic acids to form taurides (acylaminoethanesulfonates), which are used as mild anionic surfactants .
Extraction and presentation
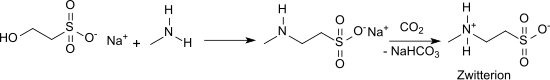
The synthesis of N -methyltaurine was reported as early as 1878, with methylamine being reacted with the silver salt of 2-chloroethanesulfonic acid. An obvious variant is the reaction of the sodium salt of 2-chloroethanesulfonic acid with methylamine. Addition of methylamine to sodium vinyl sulfonate in aqueous solution gives, after acidification with acetic acid, N -methyltaurine in 85% yield. The purification of the reaction mixture and the preparation of the N- methyltaurine can also be carried out by passing the sodium salt solution over a cation exchange resin in its H form and then over an anion exchange resin in its OH form. The reaction of sodium isethionate with methylamine in water at high temperature and pressure gives the sodium salt of N -methyltaurine,
from which pure N -methyltaurine is obtained after saturation with CO 2 and separation of the precipitated sodium hydrogen carbonate .
properties
N -methyltaurine is a white powdery solid that is easily soluble in water. The sodium salt of N -methyltaurine is also available from Chinese sources in the form of yellowish crystals and 60-65% by weight, colorless, alkaline solutions.
use
N -Methyltaurine or its sodium salt is used as a polar head group in surfactants from the class of taurides (acylaminoethanesulfonates), sometimes also called methyl taurates . The Tauride are characterized by excellent foam formation - even in the presence of oil and skin fats - and foam stability with good skin tolerance and broad pH stability. The market breakthrough for N -methyltaurine as a hair restorer is still pending.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on N-methyltaurine in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 9, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ JA Kalaitzis et al., Zwitterionic 2- (methylamino) ethanesulfonic acid , Acta Cryst. (2003). E59, o726-o727, doi : 10.1107 / S160053680300895X
- ↑ B. Lindberg, Methylated Taurines and Choline Sulfate in Red Algae , Acta Chem. Scand. , 9, 1955, pp. 1323-1326.
- ^ EW Flick, Cosmetic Additives: An Industrial Guide , Noyes Publication, Park Ridge, New Jersey, 1991, ISBN 0-8155-1255-4 , p. 352.
- ↑ Dittrich, E. (1878), About methyltaurine and the formation of methyltaurocyamine and taurocyamine , J. Prakt. Chem., 18: 63-78. doi : 10.1002 / prac.18780180102 .
- ↑ JW Schick, EF Degering, Synthesis of Taurine and N-Methyltaurine , Ind. Eng. Chem., 39, 7 (1947), pp. 906-909, doi : 10.1021 / ie50451a024 .
- ↑ Patent US7049464 : Process for producing of an aminoalkylsulfonic acid and a method of salt exchange for a salt thereof. Published on 23 May 2006 , Applicant: Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., Inventor: T. Kimura et al
- ↑ Patent US2693488 : Purification of amino alkane sulfonic acids by ion exchange. Published November 2, 1954 , Applicant: The Dow Chemical Co., Inventor: AR Sexton.
- ↑ Patent US1932907 : Published October 31, 1933 , Applicant: IG Farbenindustrie AG, Inventor: O. Nicodemus, W. Schmidt.
- ^ German Patent Office, Auslegeschrift 1 122 540; Inventor: E. Elbel et al .; Applicant: Farbwerke Hoechst AG, announced on January 27, 1962.
- ↑ Clariant brochure: Mild Surfactants , (pdf; 801 kB)
- ↑ Patent EP1235574 : Published on August 28, 2002 , Applicant: Shiseido Co. Ltd., Inventor: C. Hamada et al ..