Vinyl pyrrolidone
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
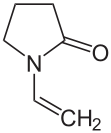
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Vinyl pyrrolidone | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 9 NO | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless to yellowish liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 111.14 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.04 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
13 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
193 ° C (53.3 k Pa ) |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure | ||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
miscible with water |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.512 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
N -Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone ( NVP ) is a colorless liquid with a weak but characteristic odor. It is a heterocyclic organic compound , but does not belong to the aromatic group. In the chemical industry it is used for the production of polymers, UV- curable coatings and inks.
Extraction and presentation
In the first synthesis step , γ-butyrolactone is reacted with ammonia . The product - 2-pyrrolidone - is then vinylated with acetylene in a Reppe synthesis .
properties
Physical Properties
With rapid cooling below a temperature of 13 ° C, vinylpyrrolidone can behave like a supercooled liquid, which is rather unusual for organic substances. If a crystallization nucleus is present, rapid exothermic crystallization then occurs , which can be confused with spontaneous polymerization . It dissolves in many organic solvents, such as. B. in acetone , diethyl ether , ethanol , toluene and benzene .
- Heat of fusion : 153 kJ / kg
- Viscosity : 2.4 m Pa (20 ° C)
- Thermal conductivity : 0.157 W / (m K) (20 ° C)
Chemical properties
Vinyl pyrrolidone is very reactive and tends to polymerize spontaneously. It must therefore be stabilized for long-term storage. Usually this is done with potassium or sodium hydroxide or an organic stabilizer such as N , N '-di- sec -butyl- p -phenylenediamine . The polymerization is also initiated by UV radiation. The heat of polymerization is −64.3 ± 1.9 kJ / mol.
Safety-related parameters
Vinylpyrrolidone forms flammable vapor-air mixtures above the flash point of 99 ° C. The explosion range is between 1.4% by volume as the lower explosion limit (LEL) and 10% by volume as the upper explosion limit (UEL). The ignition temperature is 240 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T3.
use
Due to its UV sensitivity, it is used for the production of UV-curing inks, varnishes and coatings, and as a photoinitiator for other polymers. A large number of polymers are also produced from vinyl pyrrolidone. The product range includes linear polyvinylpyrrolidones (PVP), cross-linked polyvinylpolypyrrolidone (PVPP) and numerous copolymers .
Biological importance
Vinyl pyrrolidone is classified as a category 3 carcinogen , i. H. a carcinogenic effect in humans is suspected, since an increased incidence of liver and larynx tumors was found in animal experiments.
proof
No specific method is known to detect NVP, so gas chromatography is mostly used.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Data sheet 1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone (stabilized with N, N′-di-sec-butyl-1,4-phenylenediamine) (PDF) from Merck , accessed on April 25, 2011.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k Entry on N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Data sheet 1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone, contains 100 ppm sodium hydroxide as inhibitor, ≥ 99% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on December 28, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on 1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limits - Current MAK and BAT values (search for 88-12-0 or N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone ), accessed on September 19, 2019.
- ↑ RB; Harreus, R. Backes, J.-O. Eichler, R. Feuerhake, C. Jäckel, U. Mahn, R. Pinkos, R. Vogelsang: 2-Pyrrolidone , in: Ullmanns Enzyklopädie der Technischen Chemie , Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim 2011; doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.pub2 .
- ↑ Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry , Vol. 73, No. 5, 1999, pp. 697-702.



