Nickel (II) carbonate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
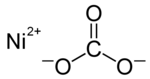
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Nickel (II) carbonate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Nickel carbonate |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | NiCO 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
light green odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 118.70 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
2.6 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
120–350 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (93 mg l −1 at 25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Nickel (II) carbonate is a chemical compound from the group of nickel compounds and carbonates which occurs in several hydrate forms.
Occurrence
Nickel (II) carbonate occurs naturally as a mineral Hellyerit (hexahydrate) and Zaratit , Nullaginit and Otwayit before (hydroxy carbonates).
Extraction and presentation
Nickel (II) carbonate-hydrates may be prepared by electrolysis of using carbon dioxide are recovered saturated water of nickel electrodes. Anhydrous nickel (II) carbonate can be obtained by reacting a sodium hydrogen carbonate solution with a nickel (II) chloride solution acidified with hydrochloric acid at high temperatures and high pressure. There is also a yellow modification that arises at different pressure, temperature and concentration ratios. Nickel (II) carbonate is also formed during the decomposition of nickel carbonyl .
properties
Nickel (II) carbonate and its hydrates are light green odorless solids that decompose at temperatures above 120 ° C into carbon dioxide and nickel (II) oxide . Anhydrous nickel (II) carbonate is insoluble in water and acids, but its hydrates are easily soluble in acids. It crystallizes rhombohedral with the space group R 3 c (space group no. 161) (a = 780.7 pm, α = 48 ° 40 '). Anhydrous nickel carbonate is difficult to produce. The nickel carbonates available on the market are basic ( nickel hydroxycarbonate, also: nickel hydroxide carbonate, NiCO 3 x Ni (OH) 2 x H 2 O, CAS number: 12607-70-4, 12122-15-5 or 12244-51-8 ) and hardly soluble in water. They arise from the precipitation of nickel salt solutions with sodium carbonate .
use
Nickel (II) carbonate is used as a catalyst in fat hardening and for the production of nickel (II) oxide, ceramic colors (pigments) and glazes as well as in electroplating .
safety instructions
Like many nickel compounds, nickel (II) carbonate is classified as carcinogenic and toxic to reproduction.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on nickel (II) carbonate in the GESTIS material database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on nickel carbonate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ a b Georg Brauer : Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry.
- ↑ a b Environmental Health Criteria (EHC) for nickel , accessed November 29, 2014.



