Nickelocene
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
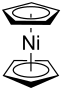
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Staggered conformation | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Nickelocene | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 10 Ni | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
dark green, crystalline solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 188.88 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
171-173 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Nickelocene ( di (cyclopentadienyl) nickel or bis (cyclopentadienyl) nickel (II) ), with the semi-structural formula [Ni (Cp) 2 ] or also [Ni (C 5 H 5 ) 2 ], is a sandwich complex , i.e. an organometallic compound with aromatic ring systems ( metallocene ). Nickelocene is structurally related to the very stable ferrocene , but unlike ferrocene , it is not air-resistant. It was first synthesized in 1953 by EO Fischer .
Binding relationships
Nickelocene consists formally of a nickel (II) cation and two cyclopentadienyl - anions (C 5 H 5 - ) together. Overall, there is an uncharged complex . The bonding conditions are similar to those of ferrocene : the cyclopentadienyl anions, as aromatics, have a delocalized π-electron system. Each of these two ligands can provide 6 π electrons to the Ni (II) cation. The nickel (II) cation itself has 8 valence electrons, so it still receives 12 electrons from the ligands, so that in the complex it has 8 + 12 = 20 valence electrons. It has two electrons more than would be favorable according to the 18-electron rule , so that these two electrons have to occupy an antibonding molecular orbital . This fact also explains the easy oxidizability of nickelocene.
properties
Nickelocene is a dark green, crystalline solid that is tolerably air-resistant and can be easily oxidized.
presentation
Nickelocene can be produced by various salt metathesis reactions, e.g. B. from sodium cyclopentadienide with nickel (II) chloride .
Analogous to ferrocene, nickelocene is accessible by reacting cyclopentadiene with nickel (II) chloride in an inert solvent and an excess of potassium hydroxide , which serves both as a deprotonation reagent for the cyclopentadiene and as a dehydrating agent:
The compound can be purified by sublimation in a vacuum at 100 ° C.
use
By treatment with nitric acid can cyclopentadienyl nickel nitrosyl be won.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Data sheet bis (cyclopentadienyl) nickel (PDF) from Strem, accessed on December 25, 2012.
- ↑ a b c data sheet bis (cyclopentadienyl) nickel (II) from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 16, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ EO Fischer, R. Jira: Di-cyclopentadienyl-nickel. In: Journal of Nature Research B . 8, 1953, pp. 217-219 ( PDF , free full text).
- ↑ a b c William L. Jolly and David J. Chazan: Bis (cyclopentadienyl) nickel (Nickelocene) . In: William L. Jolly (Ed.): Inorganic Syntheses . tape 11 . McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc., 1968, p. 122-123 (English).
- ↑ Linus Pauling: The nature of the chemical bond and the structure of molecules and crystals: an introduction to modern structural chemistry . Cornell University Press, Ithaca, NY 1960, ISBN 978-0-8014-0333-0 .
literature
- Christoph Elschenbroich : Organometallic chemistry. 6th edition, Wiesbaden 2008, ISBN 978-3-8351-0167-8 .


![{\ displaystyle {\ ce {10 KOH + 2 C5H6 + NiCl2 * 6 H2O -> [N_2] [] Ni (C5H6) 2 + 2 KCl + 8 KOH * H2O}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0aad565b85bb22d3e6e1b72cebeb2cf6be38c826)