Niobium (V) fluoride
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
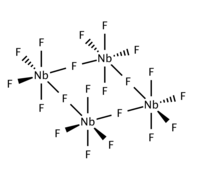
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Niobium (V) fluoride | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
Niobium pentafluoride |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | NbF 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 187.90 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
3.293 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
78.9 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
233.3 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Niobium (V) fluoride is an inorganic chemical compound of niobium from the group of fluorides .
Extraction and presentation
The first synthesis of niobium (V) fluoride was carried out by Otto Ruff and Julian Zedner at the Technical University of Danzig and submitted for publication on January 15, 1909.
Niobium (V) fluoride can be obtained by reacting niobium (V) chloride with hydrogen fluoride .
The representation from the elements is also possible:
as well as through the conversion of elemental niobium with tin (II) fluoride in a nitrogen stream at 400 to 500 ° C:
In general, like tantalum (V) fluoride , niobium (V) fluoride can be obtained from the oxides ( niobium (V) oxide ) by fluorination with fluorine or hydrogen fluoride .
properties
Niobium (V) fluoride is a colorless, very hygroscopic solid that is soluble in water and ethanol with solvolysis . It is sparingly soluble in carbon disulfide and chloroform . It hydrolyzes with alkaline solutions . The highly refractive crystals melt in air. As a solid (in contrast to the monomeric gas) the compound is present as a tetramer and has a ring structure in which four niobium atoms form an almost square parallelogram. It has a monoclinic crystal structure with the space group C 2 / m (space group no. 12) .
use
Niobium (V) fluoride can be used as a starting substance for the synthesis of niobium (IV) fluoride .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Georg Brauer (Ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler u. a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume I, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , p. 261.
- ↑ a b c Data sheet Niobium (V) fluoride, 98% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on June 20, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Otto Ruff: About some new fluorides. In: Chem. Ber. , 1909 , 42 (1), pp. 492-497 ( doi : 10.1002 / cber.19090420175 ).
- ↑ a b c Frank P. Gortsema: Niobium (IV) fluoride and niobium (V) fluoride - A. Niobium (V) fluoride . In: Aaron Wold and John K. Ruff (Eds.): Inorganic Syntheses . tape 14 . McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc., 1973, ISBN 07-071320-0 ( defective ) , p. 105-109 (English).
- ↑ Anatoly Agulyansky: Chemistry of Tantalum and Niobium Fluoride Compounds . Elsevier, 2004, ISBN 0-08-052902-X , pp. 24 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Hans Peter Latscha, Martin Mutz: Chemistry of the elements . Springer DE, 2011, ISBN 3-642-16915-5 , pp. 224 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Jean d'Ans, Ellen Lax, Roger Blachnik: Pocket book for chemists and physicists . Springer DE, 1998, ISBN 3-642-58842-5 , pp. 632 ( limited preview in Google Book search).




