Oxybuprocaine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
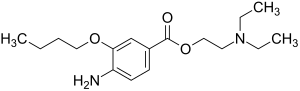
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Oxybuprocaine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 17 H 28 N 2 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 308.42 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
157-160 ° C (monohydrochloride) |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
215–218 ° C (2.7 hPa) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Monohydrochloride: soluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Oxybuprocaine is a locally effective anesthetic that is mainly used in ophthalmology (ophthalmology) and in ear, nose and throat medicine (otolaryngology). It is used in medicines as monohydrochloride . The active ingredient was patented by Wander in 1951 .
It is also used for localized inflammation in the throat and throat , often in combination with tyrothricin .
Trade names
Benoxinat (A), Cebesin (CH), Conjuncain (D), Novain (A), Novesine (D, CH), as well as a generic (CH)
Collu-Blache (CH), Fluoresceine-Oxybuprocaine (CH), Flurekain (A), Mebucaine (CH), Thilorbin (D)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on Oxybuprocaine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 20, 2019.
- ↑ a b Datasheet Benoxinate hydrochloride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 16, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ Entry on oxybuprocaine in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .