Quillaja
| Quillaja | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the family | ||||||||||||
| Quillajaceae | ||||||||||||
| D. Don | ||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the genus | ||||||||||||
| Quillaja | ||||||||||||
| Molina |
Quillaja is the only genus of the plant family of Quillajaceae within the order of the butterfly-like flowers (Fabales). The only two types are found in South America .
description
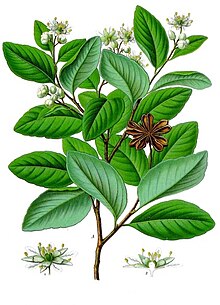
The two species of Quillaja are small, evergreen trees . The leaves , arranged in a spiral on the branches, are simple and have a serrated or serrated edge. Stipules are present.
The flowers stand together in terminal inflorescences . The hermaphroditic or functionally male, radial symmetry flowers are five-fold with a double flower envelope . There are five sepals and five petals each. There are two circles with five stamens each. It is a large, lobed discus . They have five upper, almost free carpels with free, short styles . Pollination is carried out by insects.
There are follicles formed; there are always five connected in a star shape in a pod (see photo). The seeds are winged.
Systematics and distribution
The family Quillajaceae or the genus Quillaja contains two species that are only found in South America:
- Quillaja lancifolia D.Don (Syn .: Quillaja brasiliensis (A.St.-Hil. & Tul.) Mart. And Fontenellea brasiliensis A.St.-Hil. & Tul. ) It is found in southern Brazil, northeastern Argentina and northern Uruguay is home to.
- Soap bark tree ( Quillaja saponaria Molina ), rarely also called Panama wood. It is native to warm temperate central Chile.
The genus was previously classified in the tribe Quillajeae in the subfamily of the Spiraeoideae of the family Rosaceae . That is why the species are also called soap spar.
Family tree within the order Fabales:
| Fabales |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
use
The soap bark tree ( Quillaja saponaria ) called in English "Soap bark tree" is used in folk medicine. The bark (called "panamarind"), which contains saponins , is used for soaps and above all as a shampoo. Quillaja extract (E 999) is a food additive approved in the EU , which is also obtained from the bark of the soap bark tree.
The use of the bark as sneezing powder is prohibited in Germany by the Consumer Goods Ordinance .
A purified aqueous extract - QS-21 - from the bark of the soap-bark tree contains water-soluble triterpene-glycoside compounds of the saponin family , which increase the ability of the immune system to react to vaccine antigens. QS-21 is part of the approved herpes zoster vaccine Shingrix and is also clinically tested in various vaccines for its effect as an immunological adjuvant .
literature
- K. Kubitzki : The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants. Vol.IX : Flowering Plants Eudicots , Springer, 2007, ISBN 978-3-540-322-14-6 , pp. 407 f.
- MA Bello, JA Hawkins, PJ Rudall: Floral Morphology and Development in Quillajaceae and Surianaceae (Fabales), the Species-poor Relatives of Leguminosae and Polygalaceae. In: Annals of Botany. Volume 101, Issue 3, 2008, p. 483, doi: 10.1093 / aob / mcn002 .
swell
- The family of Quillajaceae in APWebsite (Section systematics).
- The Quillajacea family in the Tree of Life project (sections description and systematics).
- Quillajaceae on the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Robyn Marty Roix, Gregory I. Vladimer u. a .: Identification of QS-21 as an Inflammasome-activating Molecular Component of Saponin Adjuvants. In: Journal of Biological Chemistry. 291, 2016, p. 1123, doi : 10.1074 / jbc.M115.683011 .