Peking mouse-ear
| Peking mouse-ear | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Myotis pequinius | ||||||||||||
| Thomas , 1908 |
The Peking mouse-ear ( Myotis pequinius ) is a type of mouse-ear ( Myotis ) within the bats (Chiroptera). It is common in parts of eastern China .
features
The Peking mouse-ear reaches a head-trunk length of about 62 millimeters and a tail length of 42 millimeters. The forearm has a length of 48 to 50 millimeters, the hind feet measure about 12 millimeters. Accordingly, it is a comparatively large species of the genus. The back fur is short and silky and gray-brown in color, the belly side is whitish. The flight skin attaches to the ankle of the feet. The outer edge of the tail flight membrane (uropatagium) is hairless or only very sparsely haired, the tail is slightly shorter than the head-trunk length. The ears are long, but when placed forward, they do not extend beyond the tip of the snout. The tragus is comparatively short and about half as long as the ear. The rear foot length is longer than half the tibial length .
The row of teeth is 14.5 millimeters long, the width of the skull is about 12.2 millimeters. The rostrum is short and curved upwards, the forehead is low and flat. The teeth have some species-specific features, the small premolars of the upper jaw are very small and lie in the row of teeth, they can also be missing.
distribution
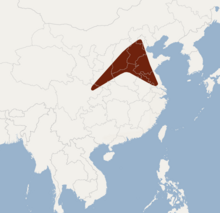
The Peking mouse-eared mouse is found in parts of the eastern People's Republic of China in Hebei , Beijing , Shandong , Sichuan , Henan and Jiangsu . It is also said to occur in Shaanxi and Anhui .
Way of life
The species is known only from a few specimens and little information is available about the way of life. The type and another bat were caught in caves, where they lived together with the long-winged bat ( Miniopterus Schreibersi ), and the species is classified as cave-living. In addition, resting places in buildings were verified. Derived from the wing shape and the calls, it is assumed that the species hunts in structured habitats, probably mainly in forests. According to the excrement samples, 80% of the food is made up of beetles , plus other insects such as bugs , butterflies and dipteras .
Systematics
The Peking mouse-eared mouse is assigned to the mouse -eared species (genus Myotis ) as a separate species , to which more than 100 species belong. The first scientific description comes from the British zoologist Oldfield Thomas from 1908, who described it based on specimens from Hebei about 50 kilometers west of Beijing. It is assigned to the Myotis subgenus within the mouse- eared species, and in some cases it was also classified in the Leuconoe or closely related to the fringed bat ( Myotis nattereri ).
No subspecies are distinguished within the species.
Hazard and protection
The species is classified by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) as not endangered ("least concern"). This assignment is justified by the large distribution area of more than 20,000 km² and the assumed large populations. There are no known threats to the species’s population. The species is likely to a certain extent adaptable to changed and disturbed habitats, as it also dorms in buildings.
supporting documents
- ↑ a b c d e f Don E. Wilson Peking Myotis. In: Andrew T. Smith , Yan Xie: A Guide to the Mammals of China. Princeton University Press, 2008; P. 379, ISBN 978-0-691-09984-2 .
- ↑ a b c d e Myotis pequinius in the Red List of Threatened Species of the IUCN 2016.2. Submitted by: AT Smith, CH Johnston, G. Jones, S. Rossiter, 2008. Retrieved November 23, 2016.
- ^ A b G. Jones, S. Parsons, SY Zhang, B. Stadelmann, P. Benda, M. Ruedi: Echolocation calls, wing shape, diet and phylogenetic diagnosis of the endemic Chinese bat Myotis pequinius. Acta Chiropterologica 8 (2), 2006: 451-463. ( Full text ( Memento of the original from April 8, 2017 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this note. )
- ^ A b Don E. Wilson & DeeAnn M. Reeder (eds.): Myotis pequinius in Mammal Species of the World. A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed), 2005
literature
- Don E. Wilson Peking Myotis. In: Andrew T. Smith , Yan Xie: A Guide to the Mammals of China. Princeton University Press, 2008; P. 379, ISBN 978-0-691-09984-2 .
Web links
- Myotis pequinius inthe IUCN 2016 Red List of Threatened Species . Submitted by: AT Smith, CH Johnston, G. Jones, S. Rossiter, 2008. Retrieved November 23, 2016.