Performic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Performic acid | |||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | CH 2 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 62.02 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Performic acid is an organic compound with the empirical formula CH 2 O 3 . It is an unstable, colorless liquid that can be made by mixing formic acid with hydrogen peroxide . Due to its oxidizing and disinfecting properties, it is used in the chemical, medical and food industries.
properties
Performic acid is a colorless liquid that is soluble in water, alcohols, ethers, benzene , chloroform and other organic solvents.
use
Their strong oxidizing properties are used to destroy disulfide bridges for protein sequencing as well as for epoxidation , hydroxylation and oxidation in organic synthesis.
Performic acid is widely used in the medical and food industries to disinfect work equipment. In this function it is effective against viruses, bacterial spores, algae, microscopic fungi, mycobacteria and other microorganisms such as zooplankton . The popularity of performic acid as a disinfectant is due to the harmlessness of its breakdown products, mainly carbon dioxide , oxygen and water. The disinfecting effect of performic acid is also more effective than that of the related compounds peracetic acid and hydrogen peroxide. The main disadvantages of performic acid are the hazards in handling due to its high reactivity and its instability, especially when heated, which results in the acid having to be used within 12 hours of its synthesis.
synthesis
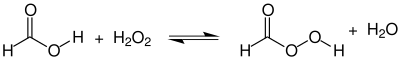
Performic acid can be represented by the reaction of formic acid with hydrogen peroxide, in which the following equilibrium reaction takes place:
The preparation of pure performic acid has not yet been reported, but aqueous solutions with concentrations of up to 48% can be prepared by simply mixing equimolar solutions of the reactants. Using an excess of one of the reactants shifts the equilibrium to the product side. The aqueous solution of the product can be distilled to achieve a concentration of about 90%.
The reaction is reversible and can be used for large-scale industrial synthesis, provided it is accelerated by a catalyst . However, the temperature must be kept below 80–85 ° C to avoid a possible explosion. Nitric acid , hydrofluoric acid , phosphoric acid , sulfuric acid or their salts can be used as the catalyst . The use of an organic compound which contains at least one ester group (e.g. carboxylic acid ester ) or peracetic acid is also possible.
Hazard warnings
Performic acid is non-toxic; it causes skin irritation, but to a lesser extent than peracetic acid. Concentrated acid above 50% is highly reactive; it decomposes quickly when heated and tends to explode when heated rapidly above 80–85 ° C. It can ignite or explode at room temperature when combined with flammable materials such as formaldehyde , benzaldehyde , or aniline , and explodes when reacting with metal powders. For this reason, spilled performic acid is diluted with cold water and absorbed with neutral, non-flammable binders, such as vermiculite .
Individual evidence
- ^ Performic acid - Lexicon of Chemistry . ( Spektrum.de ).
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ a b c d e f Daniel Swern: Organic Peracids . In: Chemical Reviews . tape 45 , no. 1 , 1949, p. 1-68 , doi : 10.1021 / cr60140a001 .
- ↑ a b c Pradyot Patnaik: A comprehensive guide to the hazardous properties of chemical substances . 3. Edition. John Wiley, Hoboken, NJ 2007, ISBN 978-0-471-71458-3 , pp. 128 .
- ^ Richard J. Simpson: Performic Acid Oxidation of Proteins . In: Cold Spring Harbor Protocols . tape 2007 , no. 3 , 2007, ISSN 1559-6095 , p. pdb.prot4698 , doi : 10.1101 / pdb.prot4698 .
- ^ R. Gehr, D. Chen, M. Moreau: Performic acid (PFA): tests on an advanced primary effluent show promising disinfection performance . In: Water Science and Technology . tape 59 , no. 1 , 2009, p. 89-96 , doi : 10.2166 / wst.2009.761 , PMID 19151490 .
- ↑ a b c Patent US6211237 : Aqueous Disinfecting Agent Containing Performic Acid and Peracetic Acid Process for Production and Process for Use Thereof. Published on April 3, 2001 , inventor: Preuss, A., Fuchs, R. Huss, M. & Schneider, R
- ↑ O. Bydžovská, V. Merka: Disinfecting properties of Performic acid against bacteriophage phi X 174 as a model of small envelope - free viruses . In: Journal of Hygiene, Epidemiology, Microbiology, and Immunology . tape 25 , no. 4 , 1981, ISSN 0022-1732 , pp. 414-423 , PMID 6459365 .
- ↑ David H. Brown Ripin, Gerald A. Weisenburger, David J. am Ende, David R. Bill, Pamela J. Clifford, Clifford N. Meltz, James E. Phillips: Execution of a Performic Acid Oxidation on Multikilogram Scale . In: Organic Process Research & Development . tape 11 , no. 4 , 2007, p. 762-765 , doi : 10.1021 / op700039r .
- ^ Barbara Elvers, Fritz Ullmann: Ullmann's encyclopedia of industrial chemistry . 5th edition. tape 19 . VCH, Weinheim [u. a.] 1991, ISBN 0-89573-169-X .
- ↑ James English, J. Delafield Gregory: Performic Acid Hydroxylation of α, β- Unsaturated Acids and Esters1 . In: Journal of the American Chemical Society . tape 69 , no. 9 , 1947, pp. 2120–2122 , doi : 10.1021 / ja01201a016 .
- ↑ Patent US6049002 : Method for the preparation of aqueous solutions containing performic acid as well as their use. Published on April 11, 2000 , inventors: Tapio Mattila, Reijo Aksela.