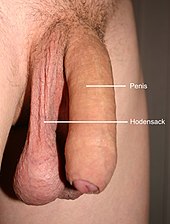
penis
The penis ( , Indo-European stem, Latin penis , "tail, male member"; cf. Greek πέος péos ; plural: penes or also penises ), technically also membrum virile ( male member ), is the term used to describe the reproductive organ of male animals in species with internal fertilization .
function
The penis is used to transfer sperm into the female genital tract and to excrete urine . He is trained mainly in terrestrial animal species as well as in sediment dwellers. The penes of different animal groups are not homologous to one another , but have arisen several times independently of one another in the course of evolution.
The human penis corresponds in its anatomy and function to the typically structured penis of mammals . As a phallus, it is an important symbol of fertility in many cultures .
Structure and occurrence
The penis is usually an unpaired tubular or channel-shaped organ that serves as an extension of the spermatic duct . In the simplest case, it is formed by a tube that is everted out as a body attachment with the help of internal body pressure and inserted into the vagina of the female animal. This shape is developed, for example, in various flatworms and rotifers and is called cirrus there .
In the case of scratch worms , many snails and annelid worms and some snakes , the penis is stabilized by a supporting tissue and horny substance . This cuticular exoskeleton stiffens the penis and provides attachment points for muscles, with the help of which the penis can be extended. In the case of many insects and other arthropods , especially crustaceans , the penis, on the other hand, is formed as a tube made of chitin and can be telescoped in and out. However, it is comparatively flexible due to its soft intercutaneous membranes. They also refer to the penis as an aedeagus .
In most vertebrates , which have a closed blood circulation , the penis does not protrude through muscles, but with the help of special cavernous bodies , which consist of connective tissue with numerous cavities. With them, the erectile tissue is filled with blood and thus lead to an erection of the penis. This form of penile erection is developed in turtles , crocodiles and the penis of mammals , but here too does not go back to a common origin. The penis of birds also has cavernous bodies, but these are filled via lymph .
A special type of penis are the rigid injection cannulas, which are formed in some jaw mouths and vortex worms . With them, the sperm is not injected into the female genital opening, but at any point in the female's body, a so-called hypodermic copulation . The sperm then reach the eggs via the body fluid and fertilize them.
Although penis formations are usually unpaired, there are also some groups of animals with paired hemipenes (half-penises). Among the invertebrates, these include the mayflies and among the vertebrates the scaled crawfish with the two hemipenes. For stimulation and a better hold, penises can be equipped with horn scales and barbs in many mammals and also in reptiles.
See also
literature
- Wilfried Westheide , Reinhard Rieger (Hrsg.): Special zoology. Part 1: Protozoa and invertebrates. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart / Jena / New York 1996.
- Wilfried Westheide, Reinhard Rieger (Hrsg.): Special zoology. Part 2: vertebrates and skulls. Spectrum Academic Publishing House, Munich 2004.
- Penis. In: Herder-Lexikon der Biologie. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg 2003, ISBN 3-8274-0354-5 .
- Kim Wallen, Elisabeth A. Lloyd: Clitoral variability compared with penile variability supports nonadaptation of female orgasm. EVOLUTION & DEVELOPMENT 10: 1, 1-2 (2008)