Polysulfone
| Structural formula | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
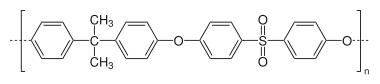
|
|||||||
| General | |||||||
| Surname | Polysulfone | ||||||
| other names |
|
||||||
| CAS number | 25135-51-7 | ||||||
| Monomers | Bisphenol A and 4,4'-dichlorodiphenyl sulfone | ||||||
| Molecular formula of the repeating unit | C 27 H 22 O 4 S | ||||||
| Molar mass of the repeating unit | 442.54 g mol −1 | ||||||
| Type of polymer | |||||||
| properties | |||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||
| Glass temperature |
180-190 ° C |
||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||
|
|||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||
Polysulfone ( abbreviation PSU) is an amorphous plastic which , as the simplest, homologous polysulfone , is counted among the high-temperature-resistant high-performance thermoplastics .
history
PSU was launched by Union Carbide in 1965 .
Manufacturing
Polysulfone is produced by multistage polycondensation of bisphenol A with 4,4'-dichlorodiphenyl sulfone.
properties
Polysulfone is crystal clear with a slight yellow tinge and is hard, stiff and tough in a range of −100 to 190 ° C.
Polysulfone has a high chemical resistance, but stress cracks occur with certain solvents. It is not resistant to ketones , aromatics , chlorinated hydrocarbons and polar solvents . It has a high resistance to β, γ, X-rays and infrared rays and permeability to microwaves . Polysulfone is broken down by UV rays below 320 nm and must therefore be stabilized against UV rays for outdoor applications. Hydroperoxide decomposers and sterically hindered amines as free radical scavengers, as well as soot, are suitable for this purpose .
The ignition temperature of polysulfone with an external flame is 475 ° C. Combustion produces mainly CO 2 , SO 2 and H 2 O and, if the oxygen supply is low, other gases. Flame spread rate and smoke development are low. For building materials, PSU has been classified in building material class B2. The oxygen index according to ISO 4589 is 32%. Unreinforced PSU was classified in class V1 according to UL94 , reinforced PSU with a thickness of 3.2 mm achieved V0.
processing
Since PSU absorbs moisture, it must be dried in a vacuum for approx. 3 to 4 hours at a maximum of 160 ° C before processing . It can be processed by extrusion , injection molding or blow molding . In injection molding, the melt temperature should be between 320 and 380 ° C and the mold temperature between 100 and 160 ° C. The shrinkage is 0.4 to 0.9%. During extrusion, the melt temperature should be 10 to 20 ° C lower. The temperature of the preform during blow molding should be between 300 and 330 ° C.
Sheets and foils can be processed by thermoforming . The forming temperature is 270 to 280 ° C. Parts made of PSU can be painted, metallized or machined. Water should be used as the coolant, as some emulsions may lead to stress cracks. Parts made of PSU can be connected by welding, riveting and gluing; all known welding processes can be used. One- or two-component adhesives based on PUR, epoxy or silicone as well as solvents such as N -methyl-2-pyrrolidone , N , N -dimethylformamide and dichloromethane are suitable for bonding . In the case of parts that are not stress relieved, however, these solvents can cause stress cracks.
use
Polysulfone is used in electrical engineering, electronics, in vehicle and mechanical engineering, for household appliances and in medical technology, when high heat resistance and transparency are required. However, it is also colored and / or reinforced with up to 30% glass fibers . With glass fibers, moduli of elasticity of up to 10,000 MPa can be achieved.
Trade names
Norms
- DIN 16839 (draft standard, 2009-11) Thermoplastic materials for pipe connectors - Polysulfone (PSU) - General quality requirements, testing
- ASTM D 7474-2008 Standard Practice for Determining Residual Stresses in Extruded or Molded Sulfone Plastic (SP) Parts by Immersion in Various Chemical Reagents
- ASTM F 702a-1998 polysulfone resin for medical purposes
- BS 2782-5 Method 540C September 30, 1988 Method for testing plastics - Optical properties and lightfastness when exposed to weathering - Determination of UV radiation using a polysulfone film
literature
- WEKA Practical Guide for Plastics Practice: Properties
- Ultrason - range overview, product features, use, guide values - BASF 8.92
- Hans Domininghaus: The plastics and their properties. 4th edition, VDI-Verlag 1992
- CAMPUS - material database
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on polysulfones. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on October 7, 2018.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Wolfgang Kaiser: Kunststoffchemie für Ingenieure From synthesis to application . Carl-Hanser-Verlag, 2015, ISBN 3-446-44774-1 , p. 494 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Wolfgang Kaiser: Kunststoffchemie für Ingenieure From synthesis to application . Carl-Hanser-Verlag, 2015, ISBN 3-446-44774-1 , p. 492–493 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
