Primaquine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
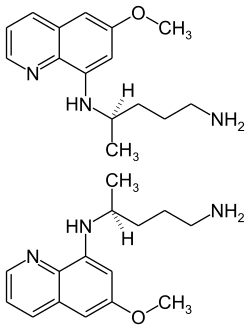
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1: 1 mixture of the stereoisomers - ( R ) -form (top) and ( S ) -form (bottom) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Primaquine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 21 N 3 O | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 259.35 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
<25 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
175-179 ° C (26.7 Pa ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Primaquine is a medicinal substance that is suitable for combating and treating malaria , especially tertian malaria.
It has been used since 1926 and is particularly effective against the extra-erythrocytic parasite stages, especially with Plasmodium vivax . The interaction of primaquine with the double-stranded DNA of the plasmodia leads to an inhibition of protein biosynthesis. The intake is limited to 2 weeks. Side effects are very rare, but serious in the case of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD deficiency). In addition, taking primaquine can lead to anemia or headaches .
The active ingredient is approved under the trade names A-PQ ® NL and Primaquine ® CDN (as of October 2009).
Side effects
During the Second World War it was noticed that African American soldiers reacted more frequently to the malaria drug primaquine with a breakdown of red blood cells (haemolysis). After the war, a defect in the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase was recognized as the cause . It also found that people from the Mediterranean area can also be affected. In addition, serious side effects are known from an interaction with grapefruit.
literature
- JK Baird, SL Hoffman: Primaquine therapy for malaria. In: Clin Infect Dis . 39, 2004, pp. 1336-1345. PMID 15494911
- Heinz Lüllmann, Klaus Mohr, Martin Wehling, Lutz Hein: Pharmacology and toxicology: Understanding drug effects - using drugs in a targeted manner. Thieme, Stuttgart.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on primaquine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 29, 2014.
- ^ A b Poisons Information Monograph (PIM) for Primaquine , accessed November 2, 2014.
- ↑ a b Entry on primaquine in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ a b Datasheet Primaquine bisphosphate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 22, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ AS Alving, PE Ccarson et al.: Enzymatic deficiency in primaquine-sensitive erythrocytes. In: Science. Volume 124, Number 3220, September 1956, pp. 484-485. PMID 13360274 .
- ↑ medicine-transparent.at