Prothioconazole
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
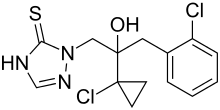
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified structural formula without stereochemistry | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Prothioconazole | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 14 H 15 Cl 2 N 3 OS | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white odorless solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 344.26 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.36 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
141.8 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
> 487 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.4 μPa (25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Prothioconazole is a mixture of two isomeric chemical compounds from the group of triazoles , more precisely the triazolinethiones .
Extraction and presentation
Prothioconazole can be obtained by reacting p -chlorobenzyl chloride with chloromethyl-1-chloro-cyclopropyl ketone and 1,2,4-triazole and reacting the intermediate product with n -butyllithium and elemental sulfur (S 8 ).
properties
Prothioconazole is a white, odorless solid that is practically insoluble in water. The technical product is a 1: 1 mixture of the two enantiomers .
use
Prothioconazole is used as a fungicide . The compound was brought onto the market by Bayer in 2002 , was approved in 2004 and works by inhibiting ergosterol biosynthesis in cell membranes.
Admission
With effect from August 1, 2008, prothioconazole was included in Annex I of Directive 91/414 / EEC and is therefore an active ingredient in plant protection products permitted for use as a fungicide in the European Union .
In many EU countries, including Germany and Austria, as well as Switzerland, plant protection products (e.g. the EfA stain ) are approved with this active ingredient.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet prothioconazole, PESTANAL at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 19, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d e F. Müller, P. Ackermann, P. Margot: Fungicides, Agricultural, 2. Individual Fungicides . In: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Technical Chemistry . Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2012, doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.o12_o06 .
- ↑ a b BVL: prothioconazole
- ^ A b Ulrich Schirmer, Peter Jeschke, Matthias Witschel: Modern Crop Protection Compounds: Herbicides . John Wiley & Sons, 2012, ISBN 978-3-527-32965-6 , pp. 791 ff . (English, limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ Peter Brandt: Reports on Plant Protection Products 2009: Active Ingredients in Plant Protection Products ; Approval history and regulations of the Plant Protection Application Ordinance . Springer, 2010, ISBN 3-0348-0029-0 , pp. 24 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Horst Börner, Klaus Schlueter: Plant diseases and plant protection . Springer, 2009, ISBN 3-540-49068-X , pp. 496 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Commission Directive 2008/44 / EC of April 4, 2008 amending Council Directive 91/414 / EEC to include the active substances benthiavalicarb, boscalid, carvone, fluoxastrobin, Paecilomyces lilacinus and prothioconazole
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on prothioconazole in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on February 23, 2016.

